Guideline-directed medical therapy for HFrEF: sequencing strategies and barriers for life-saving drug therapy
- PMID: 37311917
- PMCID: PMC10403394
- DOI: 10.1007/s10741-023-10325-2
Guideline-directed medical therapy for HFrEF: sequencing strategies and barriers for life-saving drug therapy
Abstract
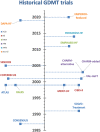
Multiple landmark trials have helped to advance the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) significantly over the past decade. These trials have led to the introduction of four main drug classes into the 2021 ESC guideline, namely angiotensin-receptor neprilysin inhibitors/angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors. The life-saving effect of these therapies has been shown to be additive and becomes apparent within weeks, which is why maximally tolerated or target doses of all drug classes should be strived for as quickly as possible. Recent evidence, such as the STRONG-HF trial, demonstrated that rapid drug implementation and up-titration is superior to the traditional and more gradual step-by-step approach where valuable time is lost to up-titration. Accordingly, multiple rapid drug implementation and sequencing strategies have been proposed to significantly reduce the time needed for the titration process. Such strategies are urgently needed since previous large-scale registries have shown that guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) implementation is a challenge. This challenge is reflected by generally low adherence rates, which can be attributed to factors considering the patient, health care system, and local hospital/health care provider. This review of the four medication classes used to treat HFrEF seeks to present a thorough overview of the data supporting current GDMT, discuss the obstacles to GDMT implementation and up-titration, and identify multiple sequencing strategies that could improve GDMT adherence. Sequencing strategies for GDMT implementation. GDMT: guideline-directed medical therapy; ACEi: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB: Angiotensin II receptor blocker; ARNi: angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor; BB: beta-blocker; MRA: mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; SGLT2i: sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor.
Keywords: Guidelines; Implementation; Pharmacotherapy; Registry; Sequencing; Titration.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J. Malgie: The author has no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. P.R.D. Clephas: The author has no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. J.J. Brugts: No relevant financial conflicts of interest. Speaker fees from Novartis, Vifor, and Abbott and advisory boards for Boerhinger, Bayer, and Astra Zenica. R.A. De Boer: received research grants and/or fees from AstraZeneca, Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardior Pharmaceuticals GmbH, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Novo Nordisk, and Roche; and has had speaker engagements with Abbott, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, and Roche. H.P. Brunner-La Rocca: unrestricted research grants from Novartis, Roche Diagnostics, Vifor; speaker fees from Boehringer-Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Vifor, Novartis, Roche Diagnostics.
Figures

References
-
- The Consensus Trial Study Group (1987) Effects of enalapril on mortality in severe congestive heart failure. Results of the Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study (CONSENSUS). N Engl J Med 316(23):1429–1435 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

