Influence of Umbilical Cord Blood Biochemical Parameters and Disease Condition on the Expression of the TSG-6 Gene in Umbilical Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- PMID: 37312421
- PMCID: PMC10278969
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.939716
Influence of Umbilical Cord Blood Biochemical Parameters and Disease Condition on the Expression of the TSG-6 Gene in Umbilical Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
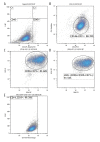
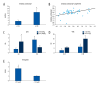
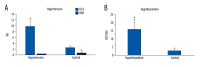
BACKGROUND Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are capable of secreting different substances, including the anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6, which can be useful in the treatment of diseases with inflammatory reactions. The main aim of this study was to evaluate the expression of the TSG-6 gene in MSCs derived from the umbilical cord. For better understanding of the anti-inflammatory properties of MSCs, we additionally assessed the expression of some interleukins (ILs). MATERIAL AND METHODS The study group included 45 patients after delivery, aged from 21 to 46 years; the average patient age was 33 years. MSCs were isolated enzymatically from umbilical cord Wharton's jelly, in vitro cultured, and characterized using flow cytometry; qPCR was performed to assess expression of the studied genes. The expression of genes of a number of pro-inflammatory ILs in MSCs was investigated in relation to the health of patients (coexistence of hypertension), the level of leukocytes, pCO2, and hemoglobin in the blood. RESULTS Our research showed that the expression of the TSG-6 gene in MSCs depends on coexisting diseases in the patient and the biochemical parameters of umbilical cord blood, including the important role of cord blood pH. We found that the levels of IL2 and IL6 expression were correlated with pCO2, and IL6 expression were correlated with pO2. CONCLUSIONS Our study suggests that maternal health status and cord blood biochemical parame-ters could affect the anti-inflammatory properties of MSCs; however, this needs to be confirmed in a future study.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human umbilical cord Wharton's Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into nerve-like cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2005 Dec 5;118(23):1987-93. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005. PMID: 16336835
-
Increased Expression of BIRC2, BIRC3, and BIRC5 from the IAP Family in Mesenchymal Stem Cells of the Umbilical Cord Wharton's Jelly (WJSC) in Younger Women Giving Birth Naturally.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Apr 8;2020:9084730. doi: 10.1155/2020/9084730. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32322338 Free PMC article.
-
[Biological characteristics of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their differentiation into neurocyte-like cells].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Jul;44(7):513-7. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17044977 Chinese.
-
Perspectives of employing mesenchymal stem cells from the Wharton's jelly of the umbilical cord for peripheral nerve repair.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2013;108:79-120. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-410499-0.00004-6. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 24083432 Review.
-
Bone and cartilage regeneration with the use of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15(11):1541-52. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2015.1068755. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26176327 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimizing Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine: Influence of Diabetes, Obesity, Autoimmune, and Inflammatory Conditions on Therapeutic Efficacy: A Review.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Aug 18;30:e945331. doi: 10.12659/MSM.945331. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 39154207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pilot Study on the Effect of Patient Condition and Clinical Parameters on Hypoxia-Induced Factor Expression: HIF1A, EPAS1 and HIF3A in Human Colostrum Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 14;25(20):11042. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011042. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pojda Z, Machaj E, Kurzyk A, et al. Mezenchymalne komórki macierzyste. Postępy Biochemii. 2013;59(2):187–97. [in Polish] - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez-Fuentes DE, Fernández-Garza LE, Samia-Meza JA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells current clinical applications: A systematic review. Arch Med Res. 2021;52(1):93–101. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

