N-Aryl Indoles as a Novel Class of Potent NaV1.7 Inhibitors
- PMID: 37312847
- PMCID: PMC10258897
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00079
N-Aryl Indoles as a Novel Class of Potent NaV1.7 Inhibitors
Abstract
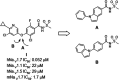
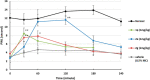
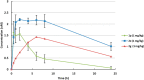
A novel class of potent NaV1.7 inhibitors has been discovered. The replacement of diaryl ether in compound I was investigated to enhance mouse NaV1.7 inhibitory activity, which resulted in the discovery of N-aryl indoles. The introduction of the 3-methyl group is crucial for high NaV1.7 in vitro potency. The adjustment of lipophilicity led to the discovery of 2e. Compound 2e (DS43260857) demonstrated high in vitro potencies against both human and mouse NaV1.7 with high selectivity over NaV1.1, NaV1.5, and hERG. In vivo evaluations revealed 2e demonstrating potent efficacy in PSL mice with excellent pharmacokinetics.
© 2023 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cox J. J.; Reimann F.; Nicholas A. K.; Thornton G.; Roberts E.; Springell K.; Karbani G.; Jafri H.; Mannan J.; Raashid Y.; Al-Gazali L.; Hamamy H.; Valente E. M.; Gorman S.; Williams R.; McHale D. P.; Wood J. N.; Gribble F. M.; Woods C. G. An SCN9A Channelopathy Causes Congenital Inability to Experience Pain. Nature 2006, 444, 894–898. 10.1038/nature05413. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McDonnell A.; Collins S.; Ali Z.; Iavarone L.; Surujbally R.; Kirby S.; Butt R. P. Efficacy of the Nav1.7 blocker PF-05089771 in a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical study in subjects with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pain 2018, 159, 1465–1476. 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001227. - DOI - PubMed
-
-
For a recent review of NaV1.7 inhibitors with the challenges, see references (−7).
-
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information

