Functional analysis of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in potato under biotic and abiotic stress
- PMID: 37312964
- PMCID: PMC10248695
- DOI: 10.1007/s11032-022-01302-y
Functional analysis of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in potato under biotic and abiotic stress
Abstract
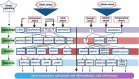
Biotic and abiotic stresses are the main constrain of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) production all over the world. To overcome these hurdles, many techniques and mechanisms have been used for increasing food demand for increasing population. One of such mechanism is mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade, which is significance regulators of MAPK pathway under various biotic and abiotic stress conditions in plants. However, the acute role in potato for various biotic and abiotic resistance is not fully understood. In eukaryotes including plants, MAPK transfer information from sensors to responses. In potato, biotic and abiotic stresses, as well as a range of developmental responses including differentiation, proliferation, and cell death in plants, MAPK plays an essential role in transduction of diverse extracellular stimuli. Different biotic and abiotic stress stimuli such as pathogen (bacteria, virus, and fungi, etc.) infections, drought, high and low temperatures, high salinity, and high or low osmolarity are induced by several MAPK cascade and MAPK gene families in potato crop. The MAPK cascade is synchronized by numerous mechanisms, including not only transcriptional regulation but also through posttranscriptional regulation such as protein-protein interactions. In this review, we will discuss the recent detailed functional analysis of certain specific MAPK gene families which are involved in resistance to various biotic and abiotic stresses in potato. This study will also provide new insights into functional analysis of various MAPK gene families in biotic and abiotic stress response as well as its possible mechanism.
Keywords: Abiotic stress; Biotic stress; MAPKs; Potato.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
StMAPK10 gene functional identification and analysis in drought resistance of potato crop (Solanum tuberosum L.).Physiol Plant. 2024 May-Jun;176(3):e14362. doi: 10.1111/ppl.14362. Physiol Plant. 2024. PMID: 38807422
-
Harnessing the role of mitogen-activated protein kinases against abiotic stresses in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Feb 24;14:932923. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.932923. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36909407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MAPK machinery in plants: recognition and response to different stresses through multiple signal transduction pathways.Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Nov;5(11):1370-8. doi: 10.4161/psb.5.11.13020. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20980831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling of the MAPK machinery activation in response to various abiotic and biotic stresses in plants by a system biology approach.Bioinformation. 2013 May 25;9(9):443-9. doi: 10.6026/97320630009443. Print 2013. Bioinformation. 2013. PMID: 23847397 Free PMC article.
-
The Function of MAPK Cascades in Response to Various Stresses in Horticultural Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jul 31;11:952. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00952. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32849671 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potato: from functional genomics to genetic improvement.Mol Hortic. 2024 Aug 19;4(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s43897-024-00105-3. Mol Hortic. 2024. PMID: 39160633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Anti-Diabetic Potential of Baicalin: Evidence from Rodent Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 28;25(1):431. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010431. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Cotton Laccase Confers Disease Resistance Against Verticillium dahliae by Promoting Cell Wall Lignification.Mol Plant Pathol. 2025 Jul;26(7):e70125. doi: 10.1111/mpp.70125. Mol Plant Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40657975 Free PMC article.
-
StMAPK1 functions as a thermos-tolerant gene in regulating heat stress tolerance in potato (Solanum tuberosum).Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jun 20;14:1218962. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1218962. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37409298 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics revealed molecular mechanism of biphenyl phytoalexin formation in response to yeast extract-induced oxidative stress in Sorbus aucuparia suspension cells.Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Feb 10;43(3):62. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03155-5. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38336832
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

