Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester With Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves Behavioral and Histopathological Changes in the Rat Model of Parkinson Disease
- PMID: 37313025
- PMCID: PMC10258596
- DOI: 10.32598/bcn.2021.1398.1
Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester With Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves Behavioral and Histopathological Changes in the Rat Model of Parkinson Disease
Abstract
Introduction: Parkinson disease (PD) results from the destruction of dopaminergic neurons in the brain. This study aimed to investigate the protective effects of natural antioxidants such as caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) to maintain these neurons.
Methods: CAPE is one of the main ingredients of propolis. Intranasal administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-2;3;4;6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) was used to generate a PD model in rats. A total of 2×bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs) were injected from the tail vein. Behavioral tests, immunohistochemistry, DiI, cresyl fast violet, and TUNEL staining were used to evaluate the rats 2 weeks after treatment.
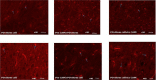
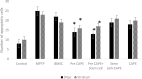
Results: In all treatment groups with stem cells, the DiI staining method revealed that the cells migrated to the substantia nigra pars compacta after injection. Treatment with CAPE significantly protects dopaminergic neurons from MPTP. The highest number of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) positive neurons was seen in the pre-CAPE+PD+stem cell (administration of CAPE, then the creation of PD, finally injection of stem cells) group. The number of TH+cells in all groups that received CAPE was significant compared to groups that received the stem cells only (P<0.001). Intranasal administration of MPTP significantly increases the number of apoptotic cells. The lowest number of apoptotic cells was in the CAPE+PD+stem cell group.
Conclusion: The results showed that the use of CAPE and stem cells in Parkinson rats caused a significant reduction in the apoptotic cells.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Caffeic acid phenethyl ester; MPTP; Parkinson disease; TUNNEL staining.
Copyright© 2022 Iranian Neuroscience Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declared no competing interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester prevents apoptotic cell death in the developing rat brain after pentylenetetrazole-induced status epilepticus.Epilepsy Behav. 2013 Nov;29(2):275-80. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2013.08.002. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Epilepsy Behav. 2013. PMID: 24012504
-
The flavanoide caffeic acid phenethyl ester blocks 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity.Neurosci Lett. 2005 Jul 22-29;383(1-2):39-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2005.04.023. Neurosci Lett. 2005. PMID: 15894425
-
Irisin protects the substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons in the rat model of Parkinson's disease.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Jul;22(7):722-728. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2019.33444.7987. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 32373292 Free PMC article.
-
Opposite effects of bone marrow-derived cells transplantation in MPTP-rat model of Parkinson's disease: a comparison study of mononuclear and mesenchymal stem cells.Int J Med Sci. 2014 Aug 3;11(10):1049-64. doi: 10.7150/ijms.8182. eCollection 2014. Int J Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 25136260 Free PMC article.
-
The intranasal administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP): a new rodent model to test palliative and neuroprotective agents for Parkinson's disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(5):489-507. doi: 10.2174/138161211795164095. Curr Pharm Des. 2011. PMID: 21375482 Review.
Cited by
-
Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Stem Cell's Perspective.Cells. 2025 Feb 27;14(5):347. doi: 10.3390/cells14050347. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40072076 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Badban L., Safari M., Sameni H. R., Bandegi A. R., Vafaei A. A., Rashidy-Pour A., et al. (2015). Protective effects of water extract of propolis on dopaminergic neurons, brain derived neurotrophic factor and stress oxidative factors in the rat model of parkinson's disease. International Journal of Pharmacology, 11(4), 300–308. [DOI:10.3923/ijp.2015.300.308] - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
