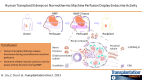
Human Transplant Kidneys on Normothermic Machine Perfusion Display Endocrine Activity
- PMID: 37313312
- PMCID: PMC10259641
- DOI: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001503
Human Transplant Kidneys on Normothermic Machine Perfusion Display Endocrine Activity
Abstract
Normothermic machine perfusion (NMP) is an alternative to hypothermic machine perfusion (HMP) for donor kidney preservation before transplantation. Contrary to HMP, NMP allows for functional assessment of donor kidneys because normothermic conditions allow for metabolic activity. The kidneys are key producers of hormones. Yet, it remains unknown whether donor kidneys during NMP display endocrine functions.
Methods: Fifteen donor kidneys were subjected to HMP followed by 2 h of NMP before transplantation. NMP perfusate was collected at 3 time points (0, 1, 2 h) for the measurements of prorenin/renin, erythropoietin (EPO), and vitamin D, and urine samples were collected at 1 h and 2 h for urodilatin measurement. Fifteen HMP perfusate samples were collected for the same measurements.
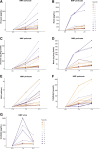
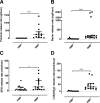
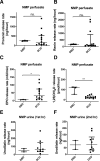
Results: Kidneys on NMP secreted significantly more prorenin, renin, EPO, and active vitamin D than during HMP. EPO and vitamin D secretion remained stable during 2 h of NMP, whereas the prorenin release rate increased and renin release rate decreased after 1 h. Donation after brain death kidneys secreted more vitamin D and less EPO during NMP than donation after circulatory death kidneys. Twelve donor kidneys produced urine during NMP and released detectable levels of urodilatin. Kidneys exhibited a large variation in hormone release rates. No significant differences were found in hormone release capacity between delayed graft function (DGF) and non-DGF kidneys, and no significant correlations were found between hormone release rates and the duration of DGF or 1-mo posttransplant serum creatinine levels.
Conclusions: Human transplant kidneys display endocrine activity during NMP. To explore whether correlations exist between hormone release rates and posttransplant kidney function, large numbers of kidneys are required.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Transplantation Direct. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no funding or conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
(Pro)renin, Erythropoietin, Vitamin D and Urodilatin Release From Human Donor Kidneys During Normothermic Machine Perfusion: Predictors of Early Post-Transplant Outcome?Clin Transplant. 2025 May;39(5):e70163. doi: 10.1111/ctr.70163. Clin Transplant. 2025. PMID: 40278798 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of normothermic and hypothermic perfusion in porcine kidneys donated after cardiac death.J Surg Res. 2017 Aug;216:35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2017.04.008. Epub 2017 Apr 20. J Surg Res. 2017. PMID: 28807212 Free PMC article.
-
Additional Normothermic Machine Perfusion Versus Hypothermic Machine Perfusion in Suboptimal Donor Kidney Transplantation: Protocol of a Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label Trial.Int J Surg Protoc. 2021 Oct 6;25(1):227-237. doi: 10.29337/ijsp.165. eCollection 2021. Int J Surg Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34708171 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing porcine donor kidney preservation with normothermic or hypothermic machine perfusion: A systematic review.Artif Organs. 2021 Nov;45(11):1308-1316. doi: 10.1111/aor.14039. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Artif Organs. 2021. PMID: 34309868 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of transplant kidneys during machine perfusion.Transpl Int. 2021 Feb;34(2):224-232. doi: 10.1111/tri.13751. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Transpl Int. 2021. PMID: 32970886 Review.
Cited by
-
(Pro)renin, Erythropoietin, Vitamin D and Urodilatin Release From Human Donor Kidneys During Normothermic Machine Perfusion: Predictors of Early Post-Transplant Outcome?Clin Transplant. 2025 May;39(5):e70163. doi: 10.1111/ctr.70163. Clin Transplant. 2025. PMID: 40278798 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Moers C, Smits JM, Maathuis MH, et al. . Machine perfusion or cold storage in deceased-donor kidney transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2009;1:7–19. - PubMed
-
- Arykbaeva AS, De Vries DK, Doppenberg JB, et al. . Metabolic needs of the kidney graft undergoing normothermic machine perfusion. Kidney Int. 2021;2:301–310. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

