Homogeneous-resolution photoacoustic microscopy for ultrawide field-of-view neurovascular imaging in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37313359
- PMCID: PMC10258506
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pacs.2023.100516
Homogeneous-resolution photoacoustic microscopy for ultrawide field-of-view neurovascular imaging in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
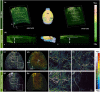
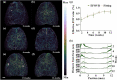
Neurovascular imaging is essential for investigating neurodegenerative diseases. However, the existing neurovascular imaging technology suffers from a trade-off between a field of view (FOV) and resolution in the whole brain, resulting in an inhomogeneous resolution and lack of information. Here, homogeneous-resolution arched-scanning photoacoustic microscopy (AS-PAM), which has an ultrawide FOV to cover the entire mouse cerebral cortex, was developed. Imaging of the neurovasculature was performed with a homogenous resolution of 6.9 µm from the superior sagittal sinus to the middle cerebral artery and caudal rhinal vein in an FOV of 12 × 12 mm2. Moreover, using AS-PAM, vascular features of the meninges and cortex were quantified in early Alzheimer's disease (AD) and wild-type (WT) mice. The results demonstrated high sensitivity to the pathological progression of AD on tortuosity and branch index. The high-fidelity imaging capability in large FOV enables AS-PAM to be a promising tool for precise brain neurovascular visualization and quantification.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Homogenous resolution; Large FOV; Neurovascular imaging; Photoacoustic microscopy.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- C.Y. Santos, P.J. Snyder, W.-C. Wu, M. Zhang, A. Echeverria, J. Alber, Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring 2017, 7 69.
-
- Sweeney M.D., Montagne A., Sagare A.P., Nation D.A., Schneider L.S., Chui H.C., Harrington M.G., Pa J., Law M., Wang D.J. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2019;15(1):158.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

