Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection Among Hospitalized Infants in Four Middle-Income Countries
- PMID: 37313727
- PMCID: PMC11268525
- DOI: 10.1093/jpids/piad042
Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection Among Hospitalized Infants in Four Middle-Income Countries
Abstract
Background: Understanding respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) global epidemiology is important to inform future prevention strategies.
Methods: Hospitalized infants <1-year-old with acute illness were enrolled prospectively in Albania, Jordan, Nicaragua, and Philippines during respiratory seasons in 2015-2017. Medical chart review, parental interview, and post-discharge follow up were conducted. Respiratory specimens were tested using real-time RT-PCR for RSV. Infant characteristics associated with very severe illness (intensive care unit [ICU] admission or receipt of supplemental oxygen) were assessed using logistic regression to adjust for potential confounders (age, sex, study site, and preterm birth).
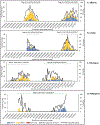
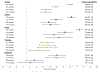
Results: Of 3634 enrolled hospitalized infants, 1129 (31%) tested positive for RSV. The median age of RSV-positive infants was 2.7 (IQR: 1.4-6.1) months and 665 (59%) were male. Very severe illness in 583 (52%) RSV-positive infants was associated with younger age (aOR 4.1, 95% CI: 2.6-6.5 for 0-2 compared to 9-11-months; P < .01), low weight-for-age z-score (aOR 1.9, 95% CI: 1.2-2.8; P < .01), ICU care after birth (aOR 1.6, 95% CI: 1.0-2.5; P = .048), and cesarean delivery (aOR 1.4, 95% CI: 1.0-1.8; P = .03). RSV subgroups A and B co-circulated at all sites with alternating predominance by year; subgroup was not associated with severity (aOR 1.0, 95% CI: 0.8-1.4). Nine (0.8%) RSV-positive infants died during admission or within ≤30 days of discharge, of which 7 (78%) were <6-months-old.
Conclusions: RSV was associated with nearly a third of infant acute illness hospitalizations in four middle-income countries during the respiratory season, where, in addition to young age, factors including low weight-for-age might be important predictors of severity. RSV prevention strategies targeting young infants could substantially reduce RSV-associated hospitalizations in middle-income countries.
Keywords: Albania; Jordan; Nicaragua; Pediatric; Philippines; Respiratory syncytial virus; bronchiolitis; global health; infant; pneumonia.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Shi T, McAllister DA, O’Brien KL, et al.; RSV Global Epidemiology Network. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: a systematic review and modelling study. Lancet 2017; 390:946–58. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Wang X, Blau DM, et al.; Respiratory Virus Global Epidemiology Network. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in children younger than 5 years in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 2022; 399:2047–64. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mazur NI, Higgins D, Nunes MC, et al. The respiratory syncytial virus vaccine landscape: lessons from the graveyard and promising candidates. Lancet Infect Dis 2018;18:e295–e311. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

