What Are the Complications, Function, and Survival of Tumor-devitalized Autografts Used in Patients With Limb-sparing Surgery for Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors? A Japanese Musculoskeletal Oncology Group Multi-institutional Study
- PMID: 37314384
- PMCID: PMC10566762
- DOI: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002720
What Are the Complications, Function, and Survival of Tumor-devitalized Autografts Used in Patients With Limb-sparing Surgery for Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors? A Japanese Musculoskeletal Oncology Group Multi-institutional Study
Abstract
Background: Tumor-devitalized autografts treated with deep freezing, pasteurization, and irradiation are biological reconstruction methods after tumor excision for aggressive or malignant bone or soft tissue tumors that involve a major long bone. Tumor-devitalized autografts do not require a bone bank, they carry no risk of viral or bacterial disease transmission, they are associated with a smaller immunologic response, and they have a better shape and size match to the site in which they are implanted. However, they are associated with disadvantages as well; it is not possible to assess margins and tumor necrosis, the devitalized bone is not normal and has limited healing potential, and the biomechanical strength is decreased owing to processing and tumor-related bone loss. Because this technique is not used in many countries, there are few reports on the results of this procedure such as complications, graft survival, and limb function.
Questions/purposes: (1) What was the rate of complications such as fracture, nonunion, infection, or recurrence in a tumor-devitalized autograft treated with deep freezing, pasteurization, and irradiation, and what factors were associated with the complication? (2) What were the 5-year and 10-year grafted bone survival (free from graft bone removal) of the three methods used to devitalize a tumor-containing autograft, and what factors were associated with grafted bone survival? (3) What was the proportion of patients with union of the tumor-devitalized autograft and what factors were associated with union of the graft-host bone junction? (4) What was the limb function after the tumor-devitalized autograft, and what factors were related to favorable limb function?
Methods: This was a retrospective, multicenter, observational study that included data from 26 tertiary sarcoma centers affiliated with the Japanese Musculoskeletal Oncology Group. From January 1993 to December 2018, 494 patients with benign or malignant tumors of the long bones were treated with tumor-devitalized autografts (using deep freezing, pasteurization, or irradiation techniques). Patients who were treated with intercalary or composite (an osteoarticular autograft with a total joint arthroplasty) tumor-devitalized autografts and followed for at least 2 years were considered eligible for inclusion. Accordingly, 7% (37 of 494) of the patients were excluded because they died within 2 years; in 19% (96), an osteoarticular graft was used, and another 10% (51) were lost to follow-up or had incomplete datasets. We did not collect information on those who died or were lost to follow-up. Considering this, 63% of the patients (310 of 494) were included in the analysis. The median follow-up was 92 months (range 24 to 348 months), the median age was 27 years (range 4 to 84), and 48% (148 of 310) were female; freezing was performed for 47% (147) of patients, pasteurization for 29% (89), and irradiation for 24% (74). The primary endpoints of this study were the cumulative incidence rate of complications and the cumulative survival of grafted bone, assessed by the Kaplan-Meier method. We used the classification of complications and graft failures proposed by the International Society of Limb Salvage. Factors relating to complications and grafted autograft removal were analyzed. The secondary endpoints were the proportion of bony union and better limb function, evaluated by the Musculoskeletal Tumor Society score. Factors relating to bony union and limb function were also analyzed. Data were investigated in each center by a record review and transferred to Kanazawa University.
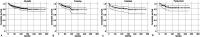
Results: The cumulative incidence rate of any complication was 42% at 5 years and 51% at 10 years. The most frequent complications were nonunion in 36 patients and infection in 34 patients. Long resection (≥ 15 cm) was associated with an increased risk of any complication based on the multivariate analyses (RR 1.8 [95% CI 1.3 to 2.5]; p < 0.01). There was no difference in the rate of complications among the three devitalizing methods. The cumulative graft survival rates were 87% at 5 years and 81% at 10 years. After controlling for potential confounding variables including sex, resection length, reconstruction type, procedure type, and chemotherapy, we found that long resection (≥ 15 cm) and composite reconstruction were associated with an increased risk of grafted autograft removal (RR 2.5 [95% CI 1.4 to 4.5]; p < 0.01 and RR 2.3 [95% CI 1.3 to 4.1]; p < 0.01). The pedicle freezing procedure showed better graft survival than the extracorporeal devitalizing procedures (94% versus 85% in 5 years; RR 3.1 [95% CI 1.1 to 9.0]; p = 0.03). No difference was observed in graft survival among the three devitalizing methods. Further, 78% (156 of 200 patients) of patients in the intercalary group and 87% (39 of 45 patients) of those in the composite group achieved primary union within 2 years. Male sex and the use of nonvascularized grafts were associated with an increased risk of nonunion (RR 2.8 [95% CI 1.3 to 6.1]; p < 0.01 and 0.28 [95% CI 0.1 to 1.0]; p = 0.04, respectively) in the intercalary group after controlling for confounding variables, including sex, site, chemotherapy, resection length, graft type, operation time, and fixation type. The median Musculoskeletal Tumor Society score was 83% (range 12% to 100%). After controlling for confounding variables including age, site, resection length, event occurrence, and graft removal, age younger than 40 years (RR 2.0 [95% CI 1.1 to 3.7]; p = 0.03), tibia (RR 6.9 [95% CI 2.7 to 17.5]; p < 0.01), femur (RR 4.8 [95% CI 1.9 to 11.7]; p < 0.01), no event (RR 2.2 [95% CI 1.1 to 4.5]; p = 0.03), and no graft removal (RR 2.9 [95% CI 1.2 to 7.3]; p = 0.03) were associated with an increased limb function. The composite graft was associated with decreased limb function (RR 0.4 [95% CI 0.2 to 0.7]; p < 0.01).
Conclusion: This multicenter study revealed that frozen, irradiated, and pasteurized tumor-bearing autografts had similar rates of complications and graft survival and all resulted in similar limb function. The recurrence rate was 10%; however, no tumor recurred with the devitalized autograft. The pedicle freezing procedure reduces the osteotomy site, which may contribute to better graft survival. Furthermore, tumor-devitalized autografts had reasonable survival and favorable limb function, which are comparable to findings reported for bone allografts. Overall, tumor-devitalized autografts are a useful option for biological reconstruction and are suitable for osteoblastic tumors or osteolytic tumors without severe loss of mechanical bone strength. Tumor-devitalized autografts could be considered when obtaining allografts is difficult and when a patient is unwilling to have a tumor prosthesis and allograft for various reasons such as cost or socioreligious reasons.
Level of evidence: Level III, therapeutic study.
Copyright © 2023 by the Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Each author certifies that there are no funding or commercial associations (consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article related to the author or any immediate family members. All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research® editors and board members are on file with the publication and can be viewed on request.
Figures
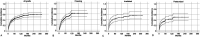

Similar articles
-
Does Augmenting Irradiated Autografts With Free Vascularized Fibula Graft in Patients With Bone Loss From a Malignant Tumor Achieve Union, Function, and Complication Rate Comparably to Patients Without Bone Loss and Augmentation When Reconstructing Intercalary Resections in the Lower Extremity?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jun 26;483(9):1680-1695. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003599. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40569278
-
Does A Single Osteotomy Technique for Frozen Autograft (Pedicled Freezing) in Patients With Malignant Bone Tumors of the Long Bones Achieve Union and Local Tumor Control?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Feb 1;482(2):340-349. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002788. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 37589950 Free PMC article.
-
Composite Reconstruction With Irradiated Autograft Plus Total Hip Replacement After Type II Pelvic Resections for Tumors Is Feasible but Fraught With Complications.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Oct 1;482(10):1825-1835. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003097. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38666740
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Conjunctival autograft for pterygium.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Feb 11;2(2):CD011349. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011349.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26867004 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Is intercalary frozen autograft augmented with intramedullary cement and bridging plates fixation a durable reconstruction?J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Nov 10;19(1):740. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05240-7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39523407 Free PMC article.
-
A reduction in tumor volume exceeding 65% predicts a good histological response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with Ewing sarcoma.Skeletal Radiol. 2024 Dec;53(12):2653-2664. doi: 10.1007/s00256-024-04702-7. Epub 2024 May 7. Skeletal Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38713225
-
Graft Infections in Biologic Reconstructions in the Oncologic Setting: A Systematic Review of the Literature.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 8;13(16):4656. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164656. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39200798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of survival, function and complication between intercalary frozen autograft versus massive allograft reconstruction after malignant bone tumors resection.J Orthop Traumatol. 2024 Nov 24;25(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s10195-024-00807-w. J Orthop Traumatol. 2024. PMID: 39581929 Free PMC article.
-
Immunologic Alteration After Total En-Bloc Spondylectomy with Anterior Spinal Column Reconstruction with Frozen Tumor-Containing Bone Autologous Grafts: A Case Report in a Prospective Study.Curr Oncol. 2025 Jul 31;32(8):432. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32080432. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40862801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdeen A, Hoang BH, Athanasian EA, Morris CD, Boland PJ, Healey JH. Allograft-prosthesis composite reconstruction of the proximal part of the humerus: functional outcome and survivorship. J Bone Joint Surg Am . 2009;91:2406-2415. - PubMed
-
- Araki N, Myoui A, Kuratsu S, et al. Intraoperative extracorporeal autogenous irradiated bone grafts in tumor surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res . 1999;368:196-206. - PubMed
-
- Araki Y, Yamamoto N, Hayashi K, et al. A viability analysis of tumor-bearing frozen autograft for the reconstruction after resection of malignant bone tumors using 99m Tc-MDP scintigraphy. Clin Nucl Med . 2023;48:25-34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

