Exogenous interleukin-1 beta stimulation regulates equine tenocyte function and gene expression in three-dimensional culture which can be rescued by pharmacological inhibition of interleukin 1 receptor, but not nuclear factor kappa B, signaling
- PMID: 37314623
- PMCID: PMC11116237
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-023-04779-z
Exogenous interleukin-1 beta stimulation regulates equine tenocyte function and gene expression in three-dimensional culture which can be rescued by pharmacological inhibition of interleukin 1 receptor, but not nuclear factor kappa B, signaling
Abstract
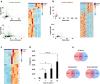
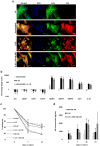
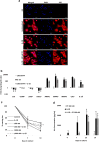
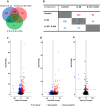
We investigated how Interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) impacts equine tenocyte function and global gene expression in vitro and determined if these effects could be rescued by pharmacologically inhibiting nuclear factor-κB (NF-KB) or interleukin 1 signalling. Equine superficial digital flexor tenocytes were cultured in three-dimensional (3D) collagen gels and stimulated with IL-1β for two-weeks, with gel contraction and interleukin 6 (IL6) measured throughout and transcriptomic analysis performed at day 14. The impact of three NF-KB inhibitors on gel contraction and IL6 secretion were measured in 3D culture, with NF-KB-P65 nuclear translocation by immunofluorescence and gene expression by qPCR measured in two-dimensional (2D) monolayer culture. In addition, daily 3D gel contraction and transcriptomic analysis was performed on interleukin 1 receptor antagonist-treated 3D gels at day 14. IL-1β increased NF-KB-P65 nuclear translocation in 2D culture and IL6 secretion in 3D culture, but reduced daily tenocyte 3D gel contraction and impacted > 2500 genes at day 14, with enrichment for NF-KB signaling. Administering direct pharmacological inhibitors of NF-KB did reduce NF-KB-P65 nuclear translocation, but had no effect on 3D gel contraction or IL6 secretion in the presence of IL-1β. However, IL1Ra restored 3D gel contraction and partially rescued global gene expression. Tenocyte 3D gel contraction and gene expression is adversely impacted by IL-1β which can only be rescued by blockade of interleukin 1 receptor, but not NF-KB, signalling.
Keywords: Cytokine; Equine; Horse; Inflammation; Musculoskeletal; Tendon.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have any competing interests to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Equine Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Tenocytes are Insensitive to a Combination of Inflammatory Cytokines and Have Distinct Molecular Responses Compared to Primary Tenocytes.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024 May;20(4):1040-1059. doi: 10.1007/s12015-024-10693-8. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024. PMID: 38396222 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mechanism for the protection of embryonic stem cell derived tenocytes from inflammatory cytokine interleukin 1 beta.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 26;9(1):2755. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39370-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30808942 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1 beta and interferon gamma have detrimental effects on equine tenocytes that cannot be rescued by IL-1RA or mesenchymal stromal cell-derived factors.Cell Tissue Res. 2023 Mar;391(3):523-544. doi: 10.1007/s00441-022-03726-6. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Cell Tissue Res. 2023. PMID: 36543895 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1β + TGF-β2 dual-licensed mesenchymal stem cells have reduced major histocompatibility class I expression and positively modulate tenocyte migration, metabolism, and gene expression.J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2024 Apr 1;262(S1):S61-S72. doi: 10.2460/javma.23.12.0708. Print 2024 Jun 1. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38547589 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1beta up-regulates RGS4 through the canonical IKK2/IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB pathway in rabbit colonic smooth muscle.Biochem J. 2008 May 15;412(1):35-43. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080042. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18260825 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advancements in Stem Cell Applications for Livestock Research: A Review.Vet Sci. 2025 Apr 23;12(5):397. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12050397. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40431490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Equine Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Tenocytes are Insensitive to a Combination of Inflammatory Cytokines and Have Distinct Molecular Responses Compared to Primary Tenocytes.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024 May;20(4):1040-1059. doi: 10.1007/s12015-024-10693-8. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024. PMID: 38396222 Free PMC article.
-
The modulating role of uniaxial straining in the IL-1β and TGF-β mediated inflammatory response of human primary ligamentocytes.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Dec 10;12:1469238. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1469238. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39720167 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

