Reduced Cerebellar BDNF Availability Affects Postnatal Differentiation and Maturation of Granule Cells in a Mouse Model of Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis
- PMID: 37314654
- PMCID: PMC10415459
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-023-03435-3
Reduced Cerebellar BDNF Availability Affects Postnatal Differentiation and Maturation of Granule Cells in a Mouse Model of Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis
Abstract
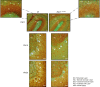
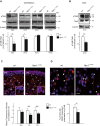
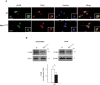
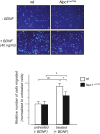
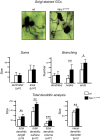
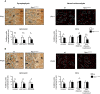
Niemann-Pick type C1 (NPC1) disease is a lysosomal lipid storage disorder due to mutations in the NPC1 gene resulting in the accumulation of cholesterol within the endosomal/lysosomal compartments. The prominent feature of the disorder is the progressive Purkinje cell degeneration leading to ataxia.In a mouse model of NPC1 disease, we have previously demonstrated that impaired Sonic hedgehog signaling causes defective proliferation of granule cells (GCs) and abnormal cerebellar morphogenesis. Studies conducted on cortical and hippocampal neurons indicate a functional interaction between Sonic hedgehog and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression, leading us to hypothesize that BDNF signaling may be altered in Npc1 mutant mice, contributing to the onset of cerebellar alterations present in NPC1 disease before the appearance of signs of ataxia.We characterized the expression/localization patterns of the BDNF and its receptor, tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB), in the early postnatal and young adult cerebellum of the Npc1nmf164 mutant mouse strain.In Npc1nmf164 mice, our results show (i) a reduced expression of cerebellar BDNF and pTrkB in the first 2 weeks postpartum, phases in which most GCs complete the proliferative/migrative program and begin differentiation; (ii) an altered subcellular localization of the pTrkB receptor in GCs, both in vivo and in vitro; (iii) reduced chemotactic response to BDNF in GCs cultured in vitro, associated with impaired internalization of the activated TrkB receptor; (iv) an overall increase in dendritic branching in mature GCs, resulting in impaired differentiation of the cerebellar glomeruli, the major synaptic complex between GCs and mossy fibers.
Keywords: Cerebellar glomerulus; Cerebellum; Niemann-Pick type C1 disease; Npc1; TrkB receptor.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Pentchev PG, Brady RO, Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Vanier MT, Carstea ED, Parker CC, Goldin E, Roff CF. The Niemann-Pick C lesion and its relationship to the intracellular distribution and utilization of LDL cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1225:235–243. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(94)90001-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Palladino G, Loizzo S, Fortuna A, Canterini S, Palombi F, Erickson RP, Mangia F, Fiorenza MT. Visual evoked potentials of Niemann-Pick type C1 mice reveal an impairment of the visual pathway that is rescued by 2-hydroxypropyl-ß-cyclodextrin. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015;10:133. doi: 10.1186/s13023-015-0348-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boyle BR, Melli SE, Altreche RS, Padron ZM, Fak Y, Kim S, Vasquez MD, Carone DM, Carone BR, Soto I. NPC1 deficiency impairs cerebellar postnatal development of microglia and climbing fiber refinement in a mouse model of Niemann-Pick disease type C. Development. 2020;147:dev189019. doi: 10.1242/dev.189019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

