Tissue Morphogenesis Through Dynamic Cell and Matrix Interactions
- PMID: 37315160
- PMCID: PMC11452922
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-020223-031019
Tissue Morphogenesis Through Dynamic Cell and Matrix Interactions
Abstract
Multicellular organisms generate tissues of diverse shapes and functions from cells and extracellular matrices. Their adhesion molecules mediate cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, which not only play crucial roles in maintaining tissue integrity but also serve as key regulators of tissue morphogenesis. Cells constantly probe their environment to make decisions: They integrate chemical and mechanical information from the environment via diffusible ligand- or adhesion-based signaling to decide whether to release specific signaling molecules or enzymes, to divide or differentiate, to move away or stay, or even whether to live or die. These decisions in turn modify their environment, including the chemical nature and mechanical properties of the extracellular matrix. Tissue morphology is the physical manifestation of the remodeling of cells and matrices by their historical biochemical and biophysical landscapes. We review our understanding of matrix and adhesion molecules in tissue morphogenesis, with an emphasis on key physical interactions that drive morphogenesis.
Keywords: basement membrane; cadherin; cell adhesion; extracellular matrix; integrin; interfacial tension.
Figures
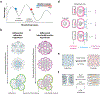
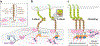

References
-
- Afratis NA, Nikitovic D, Multhaupt HAB, Theocharis AD, Couchman JR, Karamanos NK. 2017. Syndecans—key regulators of cell signaling and biological functions. FEBS J. 284(1):27–41 - PubMed
-
- Amack JD, Manning ML. 2012. Knowing the boundaries: extending the differential adhesion hypothesis in embryonic cell sorting. Science 338(6104):212–15 - PubMed
-
- Anastasiadis PZ, Moon SY, Thoreson MA, Mariner DJ, Crawford HC, et al. 2000. Inhibition of RhoA by p120 catenin. Nat. Cell Biol 2(9):637–44 - PubMed
-
- Arikawa-Hirasawa E, Watanabe H, Takami H, Hassell JR, Yamada Y. 1999. Perlecan is essential for cartilage and cephalic development. Nat. Genet 23(3):354–58 - PubMed
-
- Asai R, Taguchi E, Kume Y, Saito M, Kondo S. 1999. Zebrafish Leopard gene as a component of the putative reaction-diffusion system. Mech. Dev 89(1):87–92 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

