Effect of Brachytherapy With External Beam Radiation Therapy Versus Brachytherapy Alone for Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancer: NRG Oncology RTOG 0232 Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 37315297
- PMCID: PMC10461953
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.01856
Effect of Brachytherapy With External Beam Radiation Therapy Versus Brachytherapy Alone for Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancer: NRG Oncology RTOG 0232 Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether addition of external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) to brachytherapy (BT) (COMBO) compared with BT alone would improve 5-year freedom from progression (FFP) in intermediate-risk prostate cancer.
Methods: Men with prostate cancer stage cT1c-T2bN0M0, Gleason Score (GS) 2-6 and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) 10-20 or GS 7, and PSA < 10 were eligible. The COMBO arm was EBRT (45 Gy in 25 fractions) to prostate and seminal vesicles followed by BT prostate boost (110 Gy if 125-Iodine, 100 Gy if 103-Pd). BT arm was delivered to prostate only (145 Gy if 125-Iodine, 125 Gy if 103-Pd). The primary end point was FFP: PSA failure (American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology [ASTRO] or Phoenix definitions), local failure, distant failure, or death.
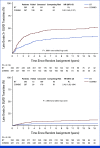
Results: Five hundred eighty-eight men were randomly assigned; 579 were eligible: 287 and 292 in COMBO and BT arms, respectively. The median age was 67 years; 89.1% had PSA < 10 ng/mL, 89.1% had GS 7, and 66.7% had T1 disease. There were no differences in FFP. The 5-year FFP-ASTRO was 85.6% (95% CI, 81.4 to 89.7) with COMBO compared with 82.7% (95% CI, 78.3 to 87.1) with BT (odds ratio [OR], 0.80; 95% CI, 0.51 to 1.26; Greenwood T P = .18). The 5-year FFP-Phoenix was 88.0% (95% CI, 84.2 to 91.9) with COMBO compared with 85.5% (95% CI, 81.3 to 89.6) with BT (OR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.49 to 1.30; Greenwood T P = .19). There were no differences in the rates of genitourinary (GU) or GI acute toxicities. The 5-year cumulative incidence for late GU/GI grade 2+ toxicity is 42.8% (95% CI, 37.0 to 48.6) for COMBO compared with 25.8% (95% CI, 20.9 to 31.0) for BT (P < .0001). The 5-year cumulative incidence for late GU/GI grade 3+ toxicity is 8.2% (95% CI, 5.4 to 11.8) compared with 3.8% (95% CI, 2.0 to 6.5; P = .006).
Conclusion: Compared with BT, COMBO did not improve FFP for prostate cancer but caused greater toxicity. BT alone can be considered as a standard treatment for men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00063882.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


References
-
- Critz FA, Tarlton RS, Holladay DA: Prostate specific antigen-monitored combination radiotherapy for patients with prostate cancer. I-125 implant followed by external-beam radiation. Cancer 75:2383-2391, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Ragde H, Elgamal AA, Snow PB, et al. : Ten-year disease free survival after transperineal sonography-guided iodine-125 brachytherapy with or without 45-gray external beam irradiation in the treatment of patients with clinically localized, low to high Gleason grade prostate carcinoma. Cancer 83:989-1001, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Blasko JC, Grimm PD, Sylvester JE, et al. : Palladium-103 brachytherapy for prostate carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 46:839-850, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Merrick GS, Butler WM, Galbreath RW, et al. : Five-year biochemical outcome following permanent interstitial brachytherapy for clinical T1-T3 prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51:41-48, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Nag S, Beyer D, Friedland J, et al. : American brachytherapy society (ABS) recommendations for transperineal permanent brachytherapy of prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 44:789-799, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

