Parallel use of human stem cell lung and heart models provide insights for SARS-CoV-2 treatment
- PMID: 37315523
- PMCID: PMC10262339
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2023.05.007
Parallel use of human stem cell lung and heart models provide insights for SARS-CoV-2 treatment
Abstract
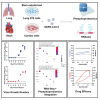
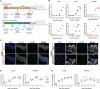
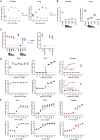
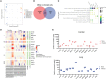
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) primarily infects the respiratory tract, but pulmonary and cardiac complications occur in severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). To elucidate molecular mechanisms in the lung and heart, we conducted paired experiments in human stem cell-derived lung alveolar type II (AT2) epithelial cell and cardiac cultures infected with SARS-CoV-2. With CRISPR-Cas9-mediated knockout of ACE2, we demonstrated that angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) was essential for SARS-CoV-2 infection of both cell types but that further processing in lung cells required TMPRSS2, while cardiac cells required the endosomal pathway. Host responses were significantly different; transcriptome profiling and phosphoproteomics responses depended strongly on the cell type. We identified several antiviral compounds with distinct antiviral and toxicity profiles in lung AT2 and cardiac cells, highlighting the importance of using several relevant cell types for evaluation of antiviral drugs. Our data provide new insights into rational drug combinations for effective treatment of a virus that affects multiple organ systems.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antiviral drugs; human stem cell-derived lung and heart models.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests E.P. is a co-founder and scientific advisor and holds equity in, and N.C. has a paid position with, Dynomics, a biotechnology company focused on the development of heart failure therapeutics. J.M.P. is a co-founder and shareholder of Mogrify, Ltd., a cell therapy company.
Figures

Update of
-
Parallel use of pluripotent human stem cell lung and heart models provide new insights for treatment of SARS-CoV-2.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 Sep 21:2022.09.20.508614. doi: 10.1101/2022.09.20.508614. bioRxiv. 2022. Update in: Stem Cell Reports. 2023 Jun 13;18(6):1308-1324. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2023.05.007. PMID: 36172136 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Anderson D.J., Kaplan D.I., Bell K.M., Koutsis K., Haynes J.M., Mills R.J., Phelan D.G., Qian E.L., Leitoguinho A.R., Arasaratnam D., et al. NKX2-5 regulates human cardiomyogenesis via a HEY2 dependent transcriptional network. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:1373. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03714-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bailey A.L., Dmytrenko O., Greenberg L., Bredemeyer A.L., Ma P., Liu J., Penna V., Winkler E.S., Sviben S., Brooks E., et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects human engineered heart tissues and models COVID-19 myocarditis. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2021;6:331–345. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2021.01.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

