Psychedelics reopen the social reward learning critical period
- PMID: 37316665
- PMCID: PMC10284704
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06204-3
Psychedelics reopen the social reward learning critical period
Abstract
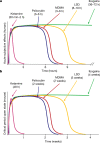
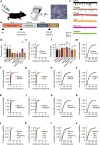
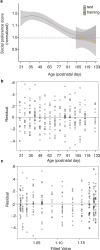
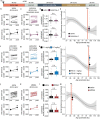
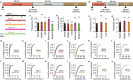
Psychedelics are a broad class of drugs defined by their ability to induce an altered state of consciousness1,2. These drugs have been used for millennia in both spiritual and medicinal contexts, and a number of recent clinical successes have spurred a renewed interest in developing psychedelic therapies3-9. Nevertheless, a unifying mechanism that can account for these shared phenomenological and therapeutic properties remains unknown. Here we demonstrate in mice that the ability to reopen the social reward learning critical period is a shared property across psychedelic drugs. Notably, the time course of critical period reopening is proportional to the duration of acute subjective effects reported in humans. Furthermore, the ability to reinstate social reward learning in adulthood is paralleled by metaplastic restoration of oxytocin-mediated long-term depression in the nucleus accumbens. Finally, identification of differentially expressed genes in the 'open state' versus the 'closed state' provides evidence that reorganization of the extracellular matrix is a common downstream mechanism underlying psychedelic drug-mediated critical period reopening. Together these results have important implications for the implementation of psychedelics in clinical practice, as well as the design of novel compounds for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disease.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
G.D. is on the scientific advisory board for Compass Pathways, Pangea Botanica and the MIND Foundation.
Figures










Comment in
-
Timing is key for behavioural benefits of psychedelics.Nature. 2023 Jun;618(7966):677-678. doi: 10.1038/d41586-023-01869-2. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37316593 No abstract available.
References
-
- Snyder, S. H. Drugs and the Brain (W. H. Freeman & Co., 1986).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

