Cerebral Semaphorin3D is a novel risk factor for age-associated cognitive impairment
- PMID: 37316917
- PMCID: PMC10265764
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-023-01158-5
Cerebral Semaphorin3D is a novel risk factor for age-associated cognitive impairment
Abstract
Background: We previously reported that miR-195 exerts neuroprotection by inhibiting Sema3A and cerebral miR-195 levels decreased with age, both of which urged us to explore the role of miR-195 and miR-195-regulated Sema3 family members in age-associated dementia.
Methods: miR-195a KO mice were used to assess the effect of miR-195 on aging and cognitive functions. Sema3D was predicted as a miR-195 target by TargetScan and then verified by luciferase reporter assay, while effects of Sema3D and miR-195 on neural senescence were assessed by beta-galactosidase and dendritic spine density. Cerebral Sema3D was over-expressed by lentivirus and suppressed by si-RNA, and effects of over-expression of Sema3D and knockdown of miR-195 on cognitive functions were assessed by Morris Water Maze, Y-maze, and open field test. The effect of Sema3D on lifespan was assessed in Drosophila. Sema3D inhibitor was developed using homology modeling and virtual screening. One-way and two-way repeated measures ANOVA were applied to assess longitudinal data on mouse cognitive tests.
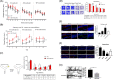
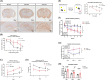
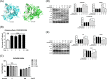
Results: Cognitive impairment and reduced density of dendritic spine were observed in miR-195a knockout mice. Sema3D was identified to be a direct target of miR-195 and a possible contributor to age-associated neurodegeneration as Sema3D levels showed age-dependent increase in rodent brains. Injection of Sema3D-expressing lentivirus caused significant memory deficits while silencing hippocampal Sema3D improved cognition. Repeated injections of Sema3D-expressing lentivirus to elevate cerebral Sema3D for 10 weeks revealed a time-dependent decline of working memory. More importantly, analysis of the data on the Gene Expression Omnibus database showed that Sema3D levels were significantly higher in dementia patients than normal controls (p < 0.001). Over-expression of homolog Sema3D gene in the nervous system of Drosophila reduced locomotor activity and lifespan by 25%. Mechanistically, Sema3D might reduce stemness and number of neural stem cells and potentially disrupt neuronal autophagy. Rapamycin restored density of dendritic spines in the hippocampus from mice injected with Sema3D lentivirus. Our novel small molecule increased viability of Sema3D-treated neurons and might improve autophagy efficiency, which suggested Sema3D could be a potential drug target. Video Abstract CONCLUSION: Our results highlight the importance of Sema3D in age-associated dementia. Sema3D could be a novel drug target for dementia treatment.
Keywords: Aging; Autophagy; Cognition; Neurodegeneration; Sema3D; miR-195.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exosomal miR-132-3p from mesenchymal stromal cells improves synaptic dysfunction and cognitive decline in vascular dementia.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jul 15;13(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02995-w. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35841005 Free PMC article.
-
Xanthohumol improves cognitive impairment by regulating miRNA-532-3p/Mpped1 in ovariectomized mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2023 May;240(5):1169-1178. doi: 10.1007/s00213-023-06355-1. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2023. PMID: 36939856
-
Aerobic exercise improves VCI through circRIMS2/miR-186/BDNF-mediated neuronal apoptosis.Mol Med. 2021 Jan 7;27(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00258-z. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33413076 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulated miR-192-5p expression rescues cognitive impairment and restores neural function in mice with depression via the Fbln2-mediated TGF-β1 signaling pathway.FASEB J. 2019 Jan;33(1):606-618. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800210RR. Epub 2018 Aug 17. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30118321
-
miR-125b promotes tau phosphorylation by targeting the neural cell adhesion molecule in neuropathological progression.Neurobiol Aging. 2019 Jan;73:41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.09.011. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Neurobiol Aging. 2019. PMID: 30316051
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Semaphorin 3A in Hippocampus Alleviates Postpartum Depression-Like Behaviors in Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun;62(6):7723-7737. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04752-5. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39934560 Free PMC article.
-
Brain transcriptomics highlight abundant gene expression and splicing alterations in non-neuronal cells in aFTLD-U.Acta Neuropathol. 2025 Aug 10;150(1):17. doi: 10.1007/s00401-025-02919-x. Acta Neuropathol. 2025. PMID: 40783910 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Case of Polymicrogyria in an Elderly Individual With Unique Polygenic Underlining.Cureus. 2024 Nov 23;16(11):e74300. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74300. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39717325 Free PMC article.
-
JC124 confers multimodal neuroprotection in epilepsy by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation: evidence from animal and human neuronal models.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jul 8;23(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02239-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40629339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnsten AFT, Datta D, Leslie S, Yang ST, Wang M, Nairn AC. Alzheimer's-like pathology in aging rhesus macaques: Unique opportunity to study the etiology and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(52):26230–38. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31871209/. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

