Combination of Shengmai San and Radix puerariae ameliorates depression-like symptoms in diabetic rats at the nexus of PI3K/BDNF/SYN protein expression
- PMID: 37317044
- PMCID: PMC10272924
- DOI: 10.1002/ame2.12333
Combination of Shengmai San and Radix puerariae ameliorates depression-like symptoms in diabetic rats at the nexus of PI3K/BDNF/SYN protein expression
Abstract
Background: Hyperglycemia is a characteristic feature of diabetes that often results in neuropsychological complications such as depression. Diabetic individuals are more vulnerable to experience depression compared to the normal population. Thus, novel treatment approaches are required to reduce depressive symptoms among diabetic individuals. Traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) such as Shengmai San (SMS) and Radix puerariae (R) are usually widely used to treat ailments such as neurological complications since ancient time.
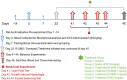
Methods: In this study, SMS was combined with R to prepare an R-SMS formulation and screened for their antidepressant activity in diabetic rats. The antidepressant potential of the prepared combination was evaluated behaviorally using open field test, novelty-induced hypophagia, and forced swim test in diabetic rats with biochemical and protein expression (PI3K, BDNF [brain-derived neurotrophic factor], and SYN [presynaptic vesicle protein]) analysis.
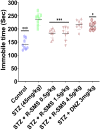
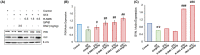
Results: Diabetic rats (streptozotocin, 45 mg/kg) showed elevated fasting blood glucose (FBG) >12 mM with depressive symptoms throughout the study. Treatment with R-SMS (0.5, 1.5, and 4.5 g/kg) significantly reverted depressive symptoms in diabetic rats as evinced by significantly (p < 0.05) reduced immobility time with an increased tendency to eat food in a novel environment. Treatment with R-SMS also significantly increased the protein expression of PI3K, BDNF, and SYN protein, which play a crucial role in depression.
Conclusion: This study showed that R-SMS formulation antagonized depressive symptoms in diabetic rats; thus, this formulation might be studied further to develop as an antidepressant.
Keywords: BDNF; STZ induced diabetes; Shengmai San; depression; traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2023 The Authors. Animal Models and Experimental Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Chinese Association for Laboratory Animal Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors read the manuscript and declared no conflict of Interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Jiawei Shengmai San herbal formula ameliorates diabetic associate cognitive decline by modulating AKT and CREB in rats.Phytother Res. 2020 Dec;34(12):3249-3261. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6773. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Phytother Res. 2020. PMID: 32619059
-
BDNF-TrkB pathway mediates antidepressant-like roles of H2 S in diabetic rats via promoting hippocampal autophagy.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020 Feb;47(2):302-312. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13201. Epub 2019 Nov 24. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31660632
-
PI3K/AKT pathway mediates the antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like roles of hydrogen sulfide in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats via promoting hippocampal neurogenesis.Neurotoxicology. 2021 Jul;85:201-208. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2021.05.016. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Neurotoxicology. 2021. PMID: 34087334
-
Geniposide alleviates depression-like behavior via enhancing BDNF expression in hippocampus of streptozotocin-evoked mice.Metab Brain Dis. 2016 Oct;31(5):1113-22. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9856-4. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Metab Brain Dis. 2016. PMID: 27311609
-
[Strategy to develop a new drug for treatment-resistant depression--role of electroconvulsive stimuli and BDNF].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007 Apr;127(4):735-42. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.127.735. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17409705 Review. Japanese.
References
-
- IDF . IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. International Diabetes Federation; 2021.
-
- Ahmed A, Zeng G, Jiang D, et al. Time‐dependent impairments in learning and memory in streptozotocin‐induced hyperglycemic rats. Metab Brain Dis. 2019;34:1431‐1446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

