Advances in Antimicrobial Peptide Discovery via Machine Learning and Delivery via Nanotechnology
- PMID: 37317103
- PMCID: PMC10223199
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11051129
Advances in Antimicrobial Peptide Discovery via Machine Learning and Delivery via Nanotechnology
Abstract
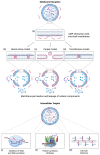
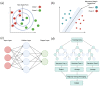
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have been investigated for their potential use as an alternative to antibiotics due to the increased demand for new antimicrobial agents. AMPs, widely found in nature and obtained from microorganisms, have a broad range of antimicrobial protection, allowing them to be applied in the treatment of infections caused by various pathogenic microorganisms. Since these peptides are primarily cationic, they prefer anionic bacterial membranes due to electrostatic interactions. However, the applications of AMPs are currently limited owing to their hemolytic activity, poor bioavailability, degradation from proteolytic enzymes, and high-cost production. To overcome these limitations, nanotechnology has been used to improve AMP bioavailability, permeation across barriers, and/or protection against degradation. In addition, machine learning has been investigated due to its time-saving and cost-effective algorithms to predict AMPs. There are numerous databases available to train machine learning models. In this review, we focus on nanotechnology approaches for AMP delivery and advances in AMP design via machine learning. The AMP sources, classification, structures, antimicrobial mechanisms, their role in diseases, peptide engineering technologies, currently available databases, and machine learning techniques used to predict AMPs with minimal toxicity are discussed in detail.
Keywords: LL-37; antibiotic resistance; antimicrobial peptide; drug delivery; machine learning; nanotechnology; peptide database; peptide design; peptide engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Machine learning for antimicrobial peptide identification and design.Nat Rev Bioeng. 2024 May;2(5):392-407. doi: 10.1038/s44222-024-00152-x. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Nat Rev Bioeng. 2024. PMID: 39850516 Free PMC article.
-
Combining genetic algorithm with machine learning strategies for designing potent antimicrobial peptides.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 May 11;22(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04156-x. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 33975547 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Prediction of Antimicrobial Peptides.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2405:1-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1855-4_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35298806 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the power of antimicrobial peptides: advances in production, optimization, and therapeutics.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Apr 28;15:1528583. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1528583. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40365533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In pursuit of next-generation therapeutics: Antimicrobial peptides against superbugs, their sources, mechanism of action, nanotechnology-based delivery, and clinical applications.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Oct 1;218:135-156. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.07.103. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 35868409 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial resistance expansion in pathogens: a review of current mitigation strategies and advances towards innovative therapy.JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2023 Dec 11;5(6):dlad127. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlad127. eCollection 2023 Dec. JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2023. PMID: 38089461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Convergence of Nanotechnology and Machine Learning: The State of the Art, Challenges, and Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 18;25(22):12368. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212368. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Bacterial Resistance to Antimicrobial Peptides in the Modern Era: An Updated Review.Microorganisms. 2024 Jun 21;12(7):1259. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071259. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide Dendrimer-Based Antibacterial Agents: Synthesis and Applications.ACS Infect Dis. 2024 Apr 12;10(4):1034-1055. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00624. Epub 2024 Mar 1. ACS Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38428037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biopreservation strategies using bacteriocins to control meat spoilage and foodborne outbreaks.Ital J Food Saf. 2024 Oct 17;13(4):12558. doi: 10.4081/ijfs.2024.12558. eCollection 2024 Nov 12. Ital J Food Saf. 2024. PMID: 39749182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2019 Antibiotic Resistance Threats Report | CDC. [(accessed on 15 December 2022)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/biggest-threats.html.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

