In Vitro and In Vivo Study of Combined Effect of Some Algerian Medicinal Plants and Probiotics against Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 37317215
- PMCID: PMC10224446
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11051242
In Vitro and In Vivo Study of Combined Effect of Some Algerian Medicinal Plants and Probiotics against Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
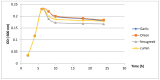
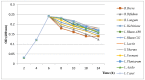
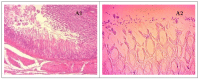
Helicobacter pylori causes gastritis, peptic ulcers and gastric cancer and affects more than half of the world's population. Although this infection can have serious consequences, no novel cure or remedy have been discovered, the present therapy still relies on a variety of known antibiotics and anti-secretory agents. In the present study, the potential effect of combinations between methanolic extracts of four Algerian medicinal plants, garlic (Allium sativum), red onion (Allium cepa), cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.) and fenugreek (T. foenum-graecum L.), with different strains of lactic acid bacteria against H. pylori, was investigated. Similarly, the in vivo antibacterial effect of fenugreek extract combined with Bifidobacterium breve on H. pylori colonization potential to confirm the enhanced effect of the mixture was explored. Helicobacter pylori was inhibited by all combined mixtures of extracts and probiotics with varying results. The highest anti-H. pylori activities were found in fenugreek/B. breve, cumin/B. breve, garlic/B. breve and onion/B. breve combinations with inhibition diameters of 29, 26, 23 and 25 mm, respectively. Preliminary studies on the effect of probiotics against H. pylori revealed that the inhibition was due to lactic acid and bacteriocins and it was also related to the presence of phenolic compounds in the studied plants, such as gallic acid, caffeic acid, quercetin and vanillic acid. Fenugreek extract was found to inhibit the growth of H. pylori in a concentration-dependent manner. When H. pylori-infected rats were administered B. breve, the infection rate of H. pylori was significantly reduced, while the combination of B. breve and fenugreek extract effectively inhibited H. pylori. In addition, the B. breve and fenugreek extract mixture significantly reduced gastritis in H. pylori-infected rats. These results suggest that this complex mixture may be an alternative to treating diseases caused by H. pylori infection.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; combined effect; cumin; fenugreek; garlic; in vivo; onion; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori by garlic extract (Allium sativum).FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1996 Apr;13(4):273-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1996.tb00251.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8739190
-
Protection against Helicobacter pylori and other bacterial infections by garlic.J Nutr. 2001 Mar;131(3s):1106S-8S. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.3.1106S. J Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11238826 Review.
-
BanXiaXieXin decoction treating gastritis mice with drug-resistant Helicobacter pylori and its mechanism.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 May 14;29(18):2818-2835. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i18.2818. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37274067 Free PMC article.
-
Bactericidal and anti-adhesive properties of culinary and medicinal plants against Helicobacter pylori.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Dec 21;11(47):7499-507. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i47.7499. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16437723 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal plant activity on Helicobacter pylori related diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug 14;20(30):10368-82. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10368. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25132753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of nanocomposites from chitosan/broccoli mucilage/selenium nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 17;14(1):21693. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65762-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39289449 Free PMC article.
-
What We Know About the Actual Role of Traditional Probiotics in Health and Disease.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Oct;16(5):1836-1856. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10275-7. Epub 2024 May 3. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 38700762 Review.
-
Ancient Remedies, Modern Medicine: A Review of Antidiabetic, Cardioprotective, and Antimicrobial Activities of Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera), Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum), and Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera).Biology (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;14(6):695. doi: 10.3390/biology14060695. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of garlic intake on atrophic gastritis risk in different infectious states of Helicobacter pylori in a case-control study.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 12;15(1):8481. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92376-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40074793 Free PMC article.
-
Role of probiotics in managing various human diseases, from oral pathology to cancer and gastrointestinal diseases.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 5;14:1296447. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1296447. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38249451 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Crowe S.E. Helicobacter infection, chronic inflammation, and the development of malignancy. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2005;21:32–38. - PubMed
-
- The IMW Group IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: International Agency for Research on Cancer. Part B: Biological Agents. 2011;Volume 100
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

