Biology and function of pericytes in the vascular microcirculation
- PMID: 37317664
- PMCID: PMC10486323
- DOI: 10.1002/ame2.12334
Biology and function of pericytes in the vascular microcirculation
Abstract
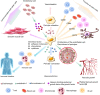
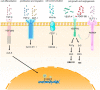
Pericytes are the main cellular components of tiny arteries and capillaries. Studies have found that pericytes can undergo morphological contraction or relaxation under stimulation by cytokines, thus affecting the contraction and relaxation of microvessels and playing an essential role in regulating vascular microcirculation. Moreover, due to the characteristics of stem cells, pericytes can differentiate into a variety of inflammatory cell phenotypes, which then affect the immune function. Additionally, pericytes can also participate in angiogenesis and wound healing by interacting with endothelial cells in vascular microcirculation disorders. Here we review the origin, biological phenotype and function of pericytes, and discuss the potential mechanisms of pericytes in vascular microcirculation disorders, especially in pulmonary hypertension, so as to provide a sound basis and direction for the prevention and treatment of vascular microcirculation diseases.
Keywords: inflammation; pericytes; pluripotency; vascular microcirculatory.
© 2023 The Authors. Animal Models and Experimental Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Chinese Association for Laboratory Animal Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelial C-Type Natriuretic Peptide Acts on Pericytes to Regulate Microcirculatory Flow and Blood Pressure.Circulation. 2018 Jul 31;138(5):494-508. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.033383. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29626067
-
Immortalized multipotent pericytes derived from the vasa vasorum in the injured vasculature. A cellular tool for studies of vascular remodeling and regeneration.Lab Invest. 2014 Dec;94(12):1340-54. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2014.121. Epub 2014 Oct 20. Lab Invest. 2014. PMID: 25329003
-
Pericyte dynamics during angiogenesis: new insights from new identities.J Vasc Res. 2014;51(3):163-74. doi: 10.1159/000362276. Epub 2014 May 17. J Vasc Res. 2014. PMID: 24853910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung Pericytes in Pulmonary Vascular Physiology and Pathophysiology.Compr Physiol. 2021 Jun 30;11(3):2227-2247. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c200027. Compr Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34190345 Free PMC article.
-
Microvascular remodeling and wound healing: a role for pericytes.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Nov;44(11):1800-12. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.06.031. Epub 2012 Jun 28. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22750474 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The machinery of healthy vasoconstriction: an overview.Pflugers Arch. 2025 Sep;477(9):1163-1189. doi: 10.1007/s00424-025-03103-6. Epub 2025 Jul 11. Pflugers Arch. 2025. PMID: 40640430 Review.
-
Pharmacological Advances in Incretin-Based Polyagonism: What We Know and What We Don't.Physiology (Bethesda). 2024 May 1;39(3):142-156. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00032.2023. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Physiology (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 38353610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimal Sca-1-based procedure for purifying mouse adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells with enhanced proliferative and differentiation potential.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 May 16;13:1566670. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1566670. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40454314 Free PMC article.
-
Pericytes in hematogenous metastasis: mechanistic insights and therapeutic approaches.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2025 Aug;48(4):921-941. doi: 10.1007/s13402-025-01073-6. Epub 2025 May 20. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2025. PMID: 40392500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Regenerative Marriage Between High-Density Platelet-Rich Plasma and Adipose Tissue.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 27;26(5):2154. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052154. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076775 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alarcon‐Martinez L, Villafranca‐Baughman D, Quintero H, et al. Interpericyte tunnelling nanotubes regulate neurovascular coupling. Nature. 2020;585(7823):91‐95. - PubMed
-
- Meijer EM, van Dijk CGM, Kramann R, Verhaar MC, Cheng C. Implementation of pericytes in vascular regeneration strategies. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022;28(1):1‐21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

