Alisol B 23-Acetate Ameliorates Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Asthma during Sensitization and Challenge Periods
- PMID: 37317820
- PMCID: PMC10616516
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2023.032
Alisol B 23-Acetate Ameliorates Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Asthma during Sensitization and Challenge Periods
Abstract
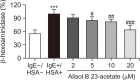
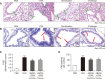
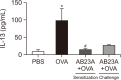
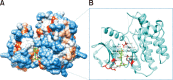
Rhizome of Alisma orientale has been used as a traditional medicine for treating kidney diseases in East Asian countries. Its inhibitory effects on hypersensitivity responses have been reported for methanol extracts, with alisol B 23-acetate (AB23Ac) being the most active constituent among six terpenes in inhibiting the direct passive Arthus reaction. However, whether AB23Ac has efficacy against allergic asthma has not been tested to date. The in vivo efficacy of AB23Ac in an ovalbumin (OVA)-induced allergic asthma mouse model was evaluated by administrating AB23Ac before OVA sensitization or OVA challenge in BALB/c mice. AB23Ac suppressed antigen-induced degranulation of RBL-2H3 mast cells in a concentration-dependent manner. The administration of AB23Ac both before OVA sensitization and OVA challenge greatly lowered pulmonary resistance and the increase in immune cell counts and inflammatory responses around the peribronchial and perivascular regions. In addition, the inflammatory cytokine levels of Th1/Th2/Th17 cells in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid decreased in the AB23Ac-treated groups. AB23Ac reduced the number of PAS-stained cells in the lungs. Furthermore, a computer modeling study indicated that AB23Ac can bind tightly to spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk). These results suggest that AB23Ac may ameliorate allergic asthma by suppressing immune responses in dendritic cells during sensitization and in mast cells during challenge periods.
Keywords: Alisol B 23-acetate; Allergy; Asthma; Immunopharmacology; Spleen tyrosine kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


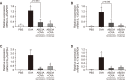
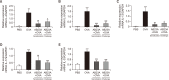
Similar articles
-
Selonsertib, an ASK1 Inhibitor, Ameliorates Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Asthma during Challenge and Sensitization Periods.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2024 Jul 1;32(4):451-459. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2023.203. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 38844790 Free PMC article.
-
NJK14047 Suppression of the p38 MAPK Ameliorates OVA-Induced Allergic Asthma during Sensitization and Challenge Periods.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023 Mar 1;31(2):183-192. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2022.078. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023. PMID: 36171179 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Free Fatty Acid Receptor 4 (FFA4) Ameliorates Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Asthma by Suppressing Activation of Dendritic and Mast Cells in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 9;23(9):5270. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095270. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563671 Free PMC article.
-
Piper nigrum extract ameliorated allergic inflammation through inhibiting Th2/Th17 responses and mast cells activation.Cell Immunol. 2017 Dec;322:64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.10.005. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Cell Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29066080
-
Total glucosides of peony improve ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma by inhibiting mast cell degranulation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Nov 15;244:112136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112136. Epub 2019 Aug 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31377261
Cited by
-
SGLT2 Inhibitors Empagliflozin and Canagliflozin Ameliorate Allergic Asthma Responses in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 10;25(14):7567. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147567. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062810 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products modulating MAPK for CRC treatment: a promising strategy.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 5;16:1514486. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1514486. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40110122 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bhatiaa M., Chaudharya J., Jaina A., Pareekb B. In: Contemporary Aadvances in Science & Technology Volume-IV. Singh R., editor. Notion Press; New Delhi: 2022. Pathophysiology and management of asthma; pp. 17–42.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

