Effectiveness of the recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring during endoscopic thyroid surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37318897
- PMCID: PMC10389580
- DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000393
Effectiveness of the recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring during endoscopic thyroid surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Thyroid disease is a common endocrine disorder, and thyroid surgeries and postoperative complications have increased recently. This study aimed to explore the effectiveness of intraoperative nerve monitoring (IONM) in endoscopic thyroid surgery using subgroup analysis and determine confounding factors.
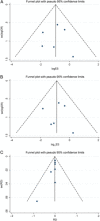
Materials and methods: Two researchers individually searched for relevant studies published till November 2022 in the PubMed, Embase, Web of Science and Cochrane Library databases. Eventually, eight studies met the inclusion criteria. Heterogeneity was assessed using the Cochran's Q test, and a funnel plot was implemented to evaluate publication bias. The odds ratio or risk difference were calculated using fixed-effects models. The weighted mean difference of continuous variables was calculated. Subgroup analysis was performed according to the disease type.
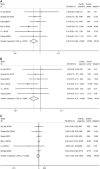
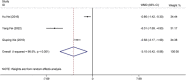
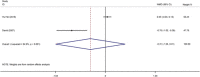
Results: Eight eligible papers included 915 patients and 1242 exposed nerves. The frequencies of transient, permanent and total recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) palsy were 2.64, 0.19 and 2.83%, respectively, in the IONM group and 6.15, 0.75 and 6.90%, respectively, in the conventional exposure group. In addition, analysis of the secondary outcome indicators for the average total length of surgery, localisation time of the RLN, recognition rate of the superior laryngeal nerve and length of incision revealed that IONM reduced the localisation time of the RLN and increased the identification rate of the superior laryngeal nerve. Subgroup analysis showed that IONM significantly reduced the incidence of RLN palsy in patients with malignancies.
Conclusions: The use of IONM significantly reduced the incidence of transient RLN palsy during endoscopic thyroid surgery, but it did not significantly reduce the incidence of permanent RLN palsy. However, the reduction in the total RLN palsy was statistically significant. In addition, IONM can effectively reduce the location time of the RLN and increase the recognition rate of the superior laryngeal nerve. Therefore, the application of IONM for malignant tumours is recommended.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article
Figures


Similar articles
-
Systematic review with meta-analysis of studies comparing intraoperative neuromonitoring of recurrent laryngeal nerves versus visualization alone during thyroidectomy.J Surg Res. 2014 May 1;188(1):152-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.12.022. Epub 2013 Dec 25. J Surg Res. 2014. PMID: 24433869
-
Intra-operative nerve monitoring and recurrent laryngeal nerve injury during thyroid surgery: a network meta-analysis of prospective studies.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2022 Dec;407(8):3209-3219. doi: 10.1007/s00423-022-02651-0. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2022. PMID: 35953619
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis on intra-operative neuro-monitoring in high-risk thyroidectomy.Int J Surg. 2017 Feb;38:21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.12.039. Epub 2016 Dec 26. Int J Surg. 2017. PMID: 28034775
-
Meta-analysis on continuous nerve monitoring in thyroidectomies.Head Neck. 2021 Dec;43(12):3966-3978. doi: 10.1002/hed.26828. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Head Neck. 2021. PMID: 34342380
-
Systematic review with meta-analysis of intraoperative neuromonitoring during thyroidectomy.Int J Surg. 2017 Mar;39:104-113. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2017.01.086. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Int J Surg. 2017. PMID: 28130189
Cited by
-
High aggressiveness of papillary thyroid cancer: from clinical evidence to regulatory cellular networks.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Aug 26;10(1):378. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02157-2. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39187514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness and feasibility of nerve real-time monitoring and intermittent monitoring in endoscopic thyroidectomy: a multicenter retrospective cohort study of 1621 patients.Int J Surg. 2025 Jan 1;111(1):904-912. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001970. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39093854 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of learning curves and related postoperative indicators between endoscopic and robotic thyroidectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2025 Jan 1;111(1):1123-1134. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001852. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 38905504 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic Revolution in Thyroid Surgery: An Umbrella Review of Clinical Outcomes.OTO Open. 2025 May 2;9(2):e70120. doi: 10.1002/oto2.70120. eCollection 2025 Apr-Jun. OTO Open. 2025. PMID: 40322312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Voice Quality and Vocal Cord Paralysis After Endarterectomy.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2024 Aug 21;20:369-375. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S465573. eCollection 2024. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2024. PMID: 39184144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dralle H. Surgical assessment of complications after thyroid gland operations. Chirurg 2015;86:70–77. - PubMed
-
- Serpell JW, Lee JC, Yeung MJ, et al. . Differential recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy rates after thyroidectomy. Surgery 2014;156:1157–1166. - PubMed
-
- Bures C, Bobak-Wieser R, Koppitsch C, et al. . Late-onset palsy of the recurrent laryngeal nerve after thyroid surgery. Br J Surg 2014;101:1556–1559. - PubMed
-
- Chiang FY, Lee KW, Chen HC, et al. . Standardization of intraoperative neuromonitoring of recurrent laryngeal nerve in thyroid operation. World J Surg 2010;34:223–229. - PubMed
-
- Dralle H, Sekulla C, Haerting J, et al. . Risk factors of paralysis and functional outcome after recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring in thyroid surgery. Surgery 2004;136:1310–1322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

