LncRNA NEAT1 Promotes Vascular Endothelial Cell Dysfunction via miR-218-5p/GAB2 and Serves as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Deep Vein Thrombosis
- PMID: 37321605
- PMCID: PMC10278436
- DOI: 10.1177/10760296231179447
LncRNA NEAT1 Promotes Vascular Endothelial Cell Dysfunction via miR-218-5p/GAB2 and Serves as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Deep Vein Thrombosis
Abstract
Objective: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a common peripheral disease. This study aimed to elucidate the diagnostic biomarker of lncRNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) in the DVT, and explore possible mechanisms in Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs).
Methods: 101 patients with lower extremity DVT and 82 healthy controls were enrolled. RT-qPCR was designed to resolve the mRNA levels of NEAT1, miR-218-5p, and GAB2. ROC was applied for the diagnosis of DVT. Systemic inflammation (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) and adhesion factor (SELP, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1) were examined by the ELISA. And cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis were conducted by the CCK-8, Transwell, flow cytometry assay. The targeting relationship was validated by Dual luciferase reporter and RIP analysis.
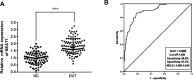
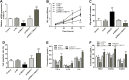
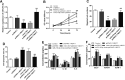
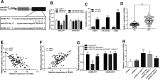
Results: NEAT1 and GAB2 were upregulated in patients with DVT, while miR-218-5p was decreased (P < .01). Serum NEAT1 can identify DVT patients from healthy individuals. NEAT1 was positively correalted with fibrinolysis factors, coagulation factors, and vasoconstrictors. NEAT1 inhibited the proliferation, migration, and promoted apoptosis as well as inflammation and adhesion factors secretion of HUVECs (P < .05), but all were impaired by overexpression of miR-218-5p (P < .05). NEAT1 promoted GAB2 expression in DVT by acting as a sponge for miR-218-5p.
Conclusion: Elevated NEAT1 is a possible DVT diagnostic biomarker, and is implicated in vascular endothelial cell dysfunction via miR-218-5p/GAB2 axis.
Keywords: HUVECs; NEAT1; deep vein thrombosis; diagnostic.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Knockdown of NEAT1 mitigates ox-LDL-induced injury in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via miR-30c-5p/TCF7 axis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Sep;24(18):9633-9644. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202009_23052. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33015807
-
Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 inhibits oxidative stress-induced vascular endothelial cell injury by activating the miR-181d-5p/CDKN3 axis.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019 Dec;47(1):3129-3137. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2019.1646264. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31352814
-
Down-regulating NEAT1 inhibited the viability and vasculogenic mimicry formation of sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma cells via miR-195-5p/VEGFA axis.Biosci Rep. 2020 Nov 27;40(11):BSR20201373. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201373. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33146672 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in microRNA regulation of deep vein thrombosis through venous vascular endothelial cells (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2024 Jun;29(6):96. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13220. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38606496 Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs regulating endothelial progenitor cells for venous thrombosis: promising therapy and innovation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Jan 2;15(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03621-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38169418 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical significance and underlying mechanism of long non-coding RNA SNHG12 in lower extremity deep venous thrombosis.Clin Transl Sci. 2024 Oct;17(10):e70023. doi: 10.1111/cts.70023. Clin Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39396235 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs: Bridging Cancer-Associated Thrombosis and Clinical Outcome of Ovarian Cancer Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 21;25(1):140. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010140. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203310 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic potential of long non-coding RNA NORAD in patients with acute deep vein thrombosis and its role in endothelial cell function.Thromb J. 2024 Jan 2;22(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12959-023-00575-3. Thromb J. 2024. PMID: 38167080 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary clinical analysis and pathway study of S100A8 as a biomarker for the diagnosis of acute deep vein thrombosis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 10;14(1):13298. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61728-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38858401 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic profiling of lncRNAs and mRNAs in a venous thrombosis mouse model.iScience. 2024 Dec 9;28(2):111561. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111561. eCollection 2025 Feb 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39949957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lu J, Fang Q, Ge X. Role and mechanism of mir-5189-3p in deep vein thrombosis of lower extremities. Ann Vasc Surg. 2021;77:288-295. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

