Cardiotocography in practice: a qualitative study to explore obstetrical care professionals' experiences with using cardiotocography information in Dutch practice
- PMID: 37321812
- PMCID: PMC10277076
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068162
Cardiotocography in practice: a qualitative study to explore obstetrical care professionals' experiences with using cardiotocography information in Dutch practice
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore obstetric care professionals' experiences with using cardiotocograph (CTG) information and how they employ this tool in their practice.
Design: Qualitative study, involving 30 semi-structured interviews and two focus group sessions. Conventional content analysis was used for data analysis.
Setting: Amsterdam University Medical Centers in the Netherlands.
Participants: In total, 43 care professionals participated. The respondents included obstetricians, residents in obstetrics and gynaecology, junior physicians, clinical midwives and nurses.
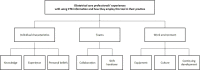
Findings: Three main categories were identified that influenced the use of cardiotocography in practice; (1) individual characteristics involving knowledge, experience and personal beliefs; (2) teams involving collaboration in and between shifts and (3) work environment involving equipment, culture and continuing development.
Conclusion: This study underlines the importance of teamwork when working with cardiotocography in practice. There is a particular need to create shared responsibility among team members for cardiotocography interpretation and appropriate management, which should be addressed in educational programmes and regular multidisciplinary meetings, to allow learning from colleagues' perspectives.
Keywords: Fetal medicine; MEDICAL EDUCATION & TRAINING; PERINATOLOGY; QUALITATIVE RESEARCH; Quality in health care.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experiences and views of midwives performing antenatal cardiotocography in Dutch primary care: A qualitative study.Midwifery. 2019 May;72:60-66. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2019.02.003. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Midwifery. 2019. PMID: 30784868
-
Cardiotocography interpretation skills and the association with size of maternity unit, years of obstetric work experience and healthcare professional background: a national cross-sectional study.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2017 Sep;96(9):1075-1083. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13171. Epub 2017 Jul 15. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2017. PMID: 28524258
-
Reliability and validity of Midwifery - Obstetrics Collaboration (MOC) scale: A tool to improve collaborative practice.Midwifery. 2021 May;96:102941. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2021.102941. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Midwifery. 2021. PMID: 33618318
-
Curriculum development for a national cardiotocography education program: a Delphi survey to obtain consensus on learning objectives.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2015 Aug;94(8):869-77. doi: 10.1111/aogs.12662. Epub 2015 May 18. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2015. PMID: 25891290
-
Midwives' and obstetricians' views on appropriate obstetric sonography in Norway.Sex Reprod Healthc. 2018 Jun;16:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.srhc.2017.12.006. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2018. PMID: 29804752 Review.
Cited by
-
Intersectional dynamics and care disparities in intrapartum electronic fetal monitoring: a socio-technical systems perspective.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Jun 2;25(1):647. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07765-z. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40457225 Free PMC article.
-
In-Depth Analysis of Caesarean Section Rate in the Largest Secondary Care-Level Maternity Hospital in Latvia.J Clin Med. 2023 Oct 9;12(19):6426. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196426. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37835069 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources