Histopathology reporting of temporal artery biopsy specimens for giant cell arteritis: results of a modified Delphi study
- PMID: 37321853
- PMCID: PMC11228225
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp-2023-208810
Histopathology reporting of temporal artery biopsy specimens for giant cell arteritis: results of a modified Delphi study
Abstract
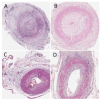
The temporal artery biopsy (TAB) is regarded as the gold-standard test in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis (GCA). There is a lack of agreement among experienced pathologists regarding the diagnostic features and classification of inflammation observed in TAB sections in the diagnosis of GCA.
Aims: The aim of this research study was to establish consensus on the key parameters which should be included in a standardised reporting proforma for TAB specimens. We specifically investigated factors pertaining to clinical information, specimen handling and microscopic pathological features.
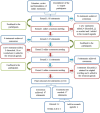
Methods: A modified Delphi process, comprising three survey rounds and three virtual consensus group meetings, was undertaken by 13 UK-based pathology or ophthalmology consultants, with a 100% response rate across the three rounds. Initial statements were formulated after a literature review and participants were asked to rate their agreement using a nine-point Likert scale. Consensus was defined a priori as an agreement of ≥70% and individual feedback was provided after each round, together with data on the distribution of group responses.
Results: Overall, 67 statements reached consensus and 17 statements did not. The participants agreed on the core microscopic features to be included in a pathology report and felt that a proforma would facilitate consistent reporting practices.
Conclusions: Our work revealed uncertainty surrounding the correlation between clinical parameters (eg, laboratory markers of inflammation and steroid therapy duration) and microscopic findings, and we propose areas for future research.
Keywords: DIAGNOSIS; INFLAMMATION; NEUROPATHOLOGY; Pathology, Surgical; VASCULITIS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SLM reports consultancy on behalf of her institution for Roche/Chugai, Sanofi, AbbVie and AstraZeneca; speaker fees received by her institution from Pfizer, Chugai and Vifor; and support from Roche to attend EULAR2019 and Pfizer to attend ACR2021.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of histopathological criteria for definite vasculitis in giant cell arteritis: retrospective analysis of temporal artery biopsies.Rheumatol Int. 2024 Nov;44(11):2547-2554. doi: 10.1007/s00296-024-05708-z. Epub 2024 Sep 8. Rheumatol Int. 2024. PMID: 39245763
-
Giant cell arteritis: diagnostic accuracy of MR imaging of superficial cranial arteries in initial diagnosis-results from a multicenter trial.Radiology. 2014 Dec;273(3):844-52. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14140056. Epub 2014 Aug 6. Radiology. 2014. PMID: 25102371 Clinical Trial.
-
The utility of the bilateral temporal artery biopsy for diagnosis of giant cell arteritis.J Vasc Surg. 2022 Dec;76(6):1704-1709. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2022.04.043. Epub 2022 Jun 13. J Vasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 35709855
-
Halo sign on temporal artery ultrasound versus temporal artery biopsy for giant cell arteritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Feb 7;2(2):CD013199. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013199.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38323659 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal artery biopsy for suspected giant cell arteritis: A mini review.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023 Oct;71(10):3299-3304. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_3163_22. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37787225 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The spectrum of giant cell arteritis through a rheumatology lens.Eye (Lond). 2024 Aug;38(12):2437-2447. doi: 10.1038/s41433-024-03153-7. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Eye (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38898105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retrospective Analysis of Specimen Quality in Temporal Artery Biopsies for Giant Cell Arteritis and Disease Association in North Midlands, England.Cureus. 2024 Aug 30;16(8):e68259. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68259. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39221306 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of histopathological criteria for definite vasculitis in giant cell arteritis: retrospective analysis of temporal artery biopsies.Rheumatol Int. 2024 Nov;44(11):2547-2554. doi: 10.1007/s00296-024-05708-z. Epub 2024 Sep 8. Rheumatol Int. 2024. PMID: 39245763
-
Variation in cystectomy pathology reporting practice-results from an international survey of 212 pathologists.Virchows Arch. 2024 Nov;485(5):879-888. doi: 10.1007/s00428-024-03924-3. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Virchows Arch. 2024. PMID: 39243298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Technology appraisal guidance Ta518. In: Tocilizumab for treating giant cell arteritis. London: NICE, 2018. Available: https:// www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta518
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical