Eukaryotic initiation factor 4 A-3 promotes glioblastoma growth and invasion through the Notch1-dependent pathway
- PMID: 37322413
- PMCID: PMC10273507
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-023-10946-8
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4 A-3 promotes glioblastoma growth and invasion through the Notch1-dependent pathway
Abstract
Background: As an adult tumor with the most invasion and the highest mortality rate, the inherent heterogeneity of glioblastoma (GBM) is the main factor that causes treatment failure. Therefore, it is important to have a deeper understanding of the pathology of GBM. Some studies have shown that Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 4A-3 (EIF4A3) can promote the growth of many people's tumors, and the role of specific molecules in GBM remains unclear.
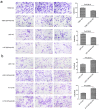
Methods: The correlation between the expression of EIF4A3 gene and its prognosis was studied in 94 GBM patients using survival analysis. Further in vitro and in vivo experiments, the effect of EIF4A3 on GBM cells proliferation, migration, and the mechanism of EIF4A3 on GBM was explored. In addition, combined with bioinformatics analysis, we further confirmed that EIF4A3 contributes to the progress of GBM.
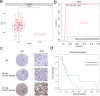
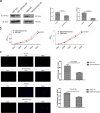
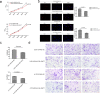
Results: The expression of EIF4A3 was upregulated in GBM tissues, and high expression of EIF4A3 is associated with poor prognosis in GBM. In vitro, knockdown of EIF4A3 significantly reduced the proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities of GBM cells, whereas overexpression of EIF4A3 led to the opposite effect. The analysis of differentially expressed genes related to EIF4A3 indicates that it is involved in many cancer-related pathways, such as Notch and JAK-STAT3 signal pathway. In Besides, we demonstrated the interaction between EIF4A3 and Notch1 by RNA immunoprecipitation. Finally, the biological function of EIF4A3-promoted GBM was confirmed in living organisms.
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that EIF4A3 may be a potential prognostic factor, and Notch1 participates in the proliferation and metastasis of GBM cells mediated by EIF4A3.
Keywords: EIF4A3; Glioblastoma; Invasion; Migration; Notch; Prognosis; Proliferation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

