Establishment and validation of a nomogram based on coagulation parameters to predict the prognosis of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 37322417
- PMCID: PMC10273637
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-023-10908-0
Establishment and validation of a nomogram based on coagulation parameters to predict the prognosis of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background: In recent years, multiple coagulation and fibrinolysis (CF) indexes have been reported to be significantly related to the progression and prognosis of some cancers.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to comprehensively analyze the value of CF parameters in prognosis prediction of pancreatic cancer (PC).
Methods: The preoperative coagulation related data, clinicopathological information, and survival data of patients with pancreatic tumor were collected retrospectively. Mann Whitney U test, Kaplan-Meier analysis, and Cox proportional hazards regression model were applied to analyze the differences of coagulation indexes between benign and malignant tumors, as well as the roles of these indexes in PC prognosis prediction.
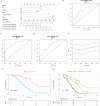
Results: Compared with benign tumors, the preoperative levels of some traditional coagulation and fibrinolysis (TCF) indexes (such as TT, Fibrinogen, APTT, and D-dimer) were abnormally increased or decreased in patients with pancreatic cancer, as well as Thromboelastography (TEG) parameters (such as R, K, α Angle, MA, and CI). Kaplan Meier survival analysis based on resectable PC patients showed that the overall survival (OS) of patients with elevated α angle, MA, CI, PT, D-dimer, or decreased PDW was markedly shorter than other patients; moreover, patients with lower CI or PT have longer disease-free survival. Further univariate and multivariate analysis revealed that PT, D-dimer, PDW, vascular invasion (VI), and tumor size (TS) were independent risk factors for poor prognosis of PC. According to the results of modeling group and validation group, the nomogram model based on independent risk factors could effectively predict the postoperative survival of PC patients.
Conclusion: Many abnormal CF parameters were remarkably correlated with PC prognosis, including α Angle, MA, CI, PT, D-dimer, and PDW. Furthermore, only PT, D-dimer, and PDW were independent prognostic indicators for poor prognosis of PC, and the prognosis prediction model based on these indicators was an effective tool to predict the postoperative survival of PC.
Keywords: Coagulation and fibrinolysis parameters; Pancreatic cancer; Predictive nomogram; Prognosis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nomogram for prognosis prediction in metastatic pancreatic cancer patients undergoing intra-arterial infusion chemotherapy: incorporating immune-inflammation scores and coagulation indicators.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jan 21;25(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13523-3. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39833690 Free PMC article.
-
Coagulation parameters for the differential diagnosis of pancreatic cancer in the early stage: a retrospective study.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Oct 17;28(1):436. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01379-x. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37848965 Free PMC article.
-
[Relationship between preoperative inflammatory indexes and prognosis of patients with rectal cancer and establishment of prognostic nomogram prediction model].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022 May 23;44(5):402-409. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200630-00612. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35615796 Chinese.
-
[Study on the value of prothrombin time for predicting the severity and prognosis of septic patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Jul;34(7):682-688. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210614-00876. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 36100403 Chinese.
-
Exploring the Prognostic Role of D-dimer Levels in Pancreatic Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Clinicopathological Associations.Cureus. 2024 Sep 4;16(9):e68627. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68627. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39371859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic value of the fibrinogen albumin ratio index (FARI) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients undergoing radiotherapy.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 23;13(1):20630. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48029-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37996660 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of Nomograms to Predict the Overall Survival and Progression-Free Survival in Patients with Advanced Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2024 Dec 18;16:1835-1849. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S489960. eCollection 2024. Cancer Manag Res. 2024. PMID: 39713568 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Coagulation Biomarkers on Survival Outcomes in Adult Glioblastoma.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Apr 19;61(4):756. doi: 10.3390/medicina61040756. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40283046 Free PMC article.
-
Hypercoagulation after neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy as a new prognostic indicator in patients with locally advanced gastric cancer undergoing surgery.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Mar 15;17(3):100927. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.100927. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40092957 Free PMC article.
-
Association of D-dimer level with thrombotic events, bleeding, and mortality in Japanese patients with solid tumors: a Cancer-VTE Registry subanalysis.Int J Clin Oncol. 2024 Apr;29(4):407-416. doi: 10.1007/s10147-024-02475-6. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Int J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38430303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aziz MH, Sideras K, Aziz NA, et al. The systemic-immune-inflammation index independently predicts survival and recurrence in Resectable Pancreatic Cancer and its Prognostic Value depends on bilirubin levels: a retrospective Multicenter Cohort Study. Ann Surg. 2019;270(1):139–46. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002660. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

