Understanding the prevalence and manifestation of anxiety and other socio-emotional and behavioural difficulties in children with Developmental Language Disorder
- PMID: 37322422
- PMCID: PMC10268478
- DOI: 10.1186/s11689-023-09486-w
Understanding the prevalence and manifestation of anxiety and other socio-emotional and behavioural difficulties in children with Developmental Language Disorder
Erratum in
-
Correction: Understanding the prevalence and manifestation of anxiety and other socio‑emotional and behavioural difficulties in children with Developmental Language Disorder.J Neurodev Disord. 2023 Jun 30;15(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s11689-023-09488-8. J Neurodev Disord. 2023. PMID: 37391724 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: It is well-documented that children with Developmental Language Disorder (DLD) have a higher likelihood of experiencing anxiety, as well as other socio-emotional and behavioural (SEB) difficulties. Despite this, there is little consensus as to how these difficulties manifest. This study aims to understand the prevalence of broader SEB difficulties and anxiety, informing intervention development by understanding the relationships between them.
Methods: A mixed-methods, case-control study was conducted. First, an online survey was completed by 107 parents of either children with DLD ("DLD sample"; n = 57) or typically developing children ("typical sample"; n = 50), aged 6-12 years old. Binary SEB statements informed by previous qualitative work (e.g. "my child requires routine/sameness"; "my child has frequent tantrums") provided an insight into the prevalence of SEB difficulties in both DLD and typical samples. Validated measures of anxiety, emotion regulation, intolerance of uncertainty, insistence on sameness, family stress and coping mechanisms were also collected. Correlation and mediation analyses were run using these validated measures to understand the manifestation of anxiety in children with DLD in more detail. Qualitative interviews were then carried out with a select panel of survey respondents (n = 4).
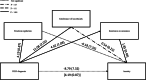
Results: The DLD sample scored significantly higher on all binary SEB statements than the typical sample: experiencing anxiety (80.7%, p < .05), requiring routine and sameness (75.4%, p < .001) and emotional dysregulation (75.4%; p < .001) were the most common difficulties reported for children with DLD. Using the validated scales, family stress and coping mechanisms were found to only correlate with the manifestation of anxiety in the typical group, not the DLD group. "Intolerance of uncertainty" and "insistence on sameness" were found to fully mediate the relationship between DLD diagnosis and symptoms of anxiety. Parent's interviews provided contextual support for the analysis, as well as highlighting sensory sensitivities as a focus for future research.
Conclusions: Parents of children with DLD appear to cope well with their children's complex SEB needs. Intervention focussing on intolerance of uncertainty may help the management of difficulties with anxiety. Behaviours such as insistence on sameness should be investigated further, as potential indicators for anxiety amongst children with DLD.
Keywords: Anxiety; Children; Developmental Language Disorder; Emotion regulation; Parents; Socio-emotional behaviour; Specific Language Impairment.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Engage with Developmental Language Disorder (E-DLD) project: Cohort profile.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023 May;58(3):929-943. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12835. Epub 2022 Dec 24. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023. PMID: 36565246
-
The role of linguistic and cognitive factors in emotion recognition difficulties in children with ASD, ADHD or DLD.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2020 Mar;55(2):231-242. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12514. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2020. PMID: 31797474
-
Exploring the Psychosocial Experiences of Individuals with Developmental Language Disorder During Childhood: A Qualitative Investigation.J Autism Dev Disord. 2024 Aug;54(8):3008-3027. doi: 10.1007/s10803-023-05946-3. Epub 2023 Jun 20. J Autism Dev Disord. 2024. PMID: 37338728 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic scoping review on contextual factors associated with communicative participation among children with developmental language disorder.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023 Mar;58(2):482-515. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12787. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023. PMID: 36239148
-
Social-Emotional Functioning and Quality of Life in Language Disorders: A Systematic Review of Development From Childhood to Adolescence.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025 May-Jun;60(3):e70039. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.70039. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025. PMID: 40260753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
"They don't realise how hard he has to try every day": The rewards and challenges of parenting a child with developmental language disorder.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025 Mar-Apr;60(2):e70003. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.70003. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025. PMID: 39970424 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of developmental language disorders on mental health and well-being across the lifespan: a qualitative study including the perspectives of UK adults with DLD and Australian speech-language therapists.BMJ Open. 2024 Oct 22;14(10):e087532. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-087532. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39438095 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and validity estimation of Urdu version of Children Emotion Management Scales (CEMS) in Pakistan.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Mar 28;14:1214708. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1214708. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38605884 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Parental Understanding of Emotions in Children with Developmental Language Disorder: An Online Parent-Led Intervention Program.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Aug 8;12(16):1571. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12161571. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39201130 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: Understanding the prevalence and manifestation of anxiety and other socio‑emotional and behavioural difficulties in children with Developmental Language Disorder.J Neurodev Disord. 2023 Jun 30;15(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s11689-023-09488-8. J Neurodev Disord. 2023. PMID: 37391724 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

