The beneficial effects of commensal E. coli for colon epithelial cell recovery are related with Formyl peptide receptor 2 (Fpr2) in epithelial cells
- PMID: 37322488
- PMCID: PMC10268441
- DOI: 10.1186/s13099-023-00557-w
The beneficial effects of commensal E. coli for colon epithelial cell recovery are related with Formyl peptide receptor 2 (Fpr2) in epithelial cells
Erratum in
-
Correction: The beneficial effects of commensal E. coli for colon epithelial cell recovery are related with Formyl peptide receptor 2 (Fpr2) in epithelial cells.Gut Pathog. 2023 Nov 30;15(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13099-023-00585-6. Gut Pathog. 2023. PMID: 38037170 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Formyl peptide receptor 2 (Fpr2) plays a crucial role in colon homeostasis and microbiota balance. Commensal E. coli is known to promote the regeneration of damaged colon epithelial cells. The aim of the study was to investigate the connection between E. coli and Fpr2 in the recovery of colon epithelial cells.
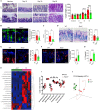
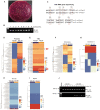
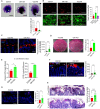
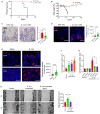
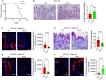
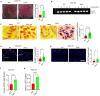
Results: The deficiency of Fpr2 was associated with impaired integrity of the colon mucosa and an imbalance of microbiota, characterized by the enrichment of Proteobacteria in the colon. Two serotypes of E. coli, O22:H8 and O91:H21, were identified in the mouse colon through complete genome sequencing. E. coli O22:H8 was found to be prevalent in the gut of mice and exhibited lower virulence compared to O91:H21. Germ-free (GF) mice that were pre-orally inoculated with E. coli O22:H8 showed reduced susceptibility to chemically induced colitis, increased proliferation of epithelial cells, and improved mouse survival. Following infection with E. coli O22:H8, the expression of Fpr2 in colon epithelial cells was upregulated, and the products derived from E. coli O22:H8 induced migration and proliferation of colon epithelial cells through Fpr2. Fpr2 deficiency increased susceptibility to chemically induced colitis, delayed the repair of damaged colon epithelial cells, and heightened inflammatory responses. Additionally, the population of E. coli was observed to increase in the colons of Fpr2-/- mice with colitis.
Conclusion: Commensal E. coli O22:H8 stimulated the upregulation of Fpr2 expression in colon epithelial cells, and the products from E. coli induced migration and proliferation of colon epithelial cells through Fpr2. Fpr2 deficiency led to an increased E. coli population in the colon and delayed recovery of damaged colon epithelial cells in mice with colitis. Therefore, Fpr2 is essential for the effects of commensal E. coli on colon epithelial cell recovery.
Keywords: Colitis; Commensal E. coli; Fpr2 −/− mice; Germ-free mice; Regeneration.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correction: The beneficial effects of commensal E. coli for colon epithelial cell recovery are related with Formyl peptide receptor 2 (Fpr2) in epithelial cells.Gut Pathog. 2023 Nov 30;15(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13099-023-00585-6. Gut Pathog. 2023. PMID: 38037170 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) O22:H8 isolated from cattle reduces E. coli O157:H7 adherence in vitro and in vivo.Vet Microbiol. 2017 Sep;208:8-17. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.06.021. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Vet Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28888654
-
Formyl peptide receptor 2 orchestrates mucosal protection against Citrobacter rodentium infection.Virulence. 2019 Dec;10(1):610-624. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2019.1635417. Virulence. 2019. PMID: 31234710 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome sequencing and experiments reveal the effect of formyl peptide receptor 2 on liver homeostasis.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jun 28;29(24):3793-3806. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i24.3793. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37426322 Free PMC article.
-
Development, validation and implementation of an in vitro model for the study of metabolic and immune function in normal and inflamed human colonic epithelium.Dan Med J. 2015 Jan;62(1):B4973. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25557335 Review.
Cited by
-
Correction: The beneficial effects of commensal E. coli for colon epithelial cell recovery are related with Formyl peptide receptor 2 (Fpr2) in epithelial cells.Gut Pathog. 2023 Nov 30;15(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13099-023-00585-6. Gut Pathog. 2023. PMID: 38037170 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Bioactive Compounds as Modulators of N-Formyl Peptide Signaling in Chronic Diseases.Molecules. 2025 Jul 16;30(14):2981. doi: 10.3390/molecules30142981. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40733247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formyl peptide receptor 2: a potential therapeutic target for inflammation-related diseases.Pharmacol Rep. 2025 Jun;77(3):593-609. doi: 10.1007/s43440-025-00704-x. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Pharmacol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40102363 Review.
References
-
- Martinez JE, Kahana DD, Ghuman S, Wilson HP, Wilson J, Kim SCJ, Lagishetty V, Jacobs JP, Sinha-Hikim AP, Friedman TC. Unhealthy lifestyle and gut dysbiosis: a better understanding of the effects of poor diet and nicotine on the intestinal microbiome. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021;12:667066. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.667066. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

