Stability of polymeric cationic niosomes and their plasmid DNA-based complexes as gene delivery carriers
- PMID: 37322900
- PMCID: PMC10281300
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2219420
Stability of polymeric cationic niosomes and their plasmid DNA-based complexes as gene delivery carriers
Abstract
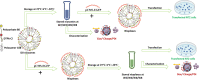
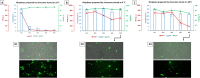
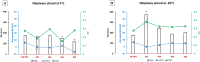
This study aims to explore the stability of lipo-polymeric niosomes/niosome-based pCMS-EGFP complexes under different storage temperatures (25 °C, 4 °C, and -20 °C). To date, the question of nucleic acid-complex stability is one of the most vital issues in gene delivery applications. The need for stable vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic has merely highlighted it. In the case of niosomes as gene carriers, the scientific literature still lacks comprehensive stability studies. In this study, the physicochemical features of niosomes/nioplexes in terms of size, surface charge, and polydispersity index (PDI), along with transfection efficiency, and cytotoxicity in NT2 cells were evaluated for 8 weeks. Compared to day 0, the physicochemical features of the niosomes stored at 25 °C and -20 °C changed dramatically in terms of size, zeta potential, and PDI, while remaining in reasonable values when stored at 4 °C. However, niosomes and nioplexes stored at 4 °C and -20 °C showed nearly stable transfection efficiency values, yet an obvious decrease at 25 °C. This article provides a proof of concept into the stability of polymeric cationic niosomes and their nioplexes as promising gene delivery vehicles. Moreover, it highlights the practical possibility of storing nioplexes at 4 °C for up to 2 months, as an alternative to niosomes, for gene delivery purposes.
Keywords: Stability; cationic niosome; gene delivery; nioplexes; non-viral vectors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The influence of the polar head-group of synthetic cationic lipids on the transfection efficiency mediated by niosomes in rat retina and brain.Biomaterials. 2016 Jan;77:267-79. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.11.017. Epub 2015 Nov 14. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 26610076
-
Polysorbate 20 non-ionic surfactant enhances retinal gene delivery efficiency of cationic niosomes after intravitreal and subretinal administration.Int J Pharm. 2018 Oct 25;550(1-2):388-397. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.07.035. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Int J Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30009984
-
Elaboration and Physicochemical Characterization of Niosome-Based Nioplexes for Gene Delivery Purposes.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1445:63-75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3718-9_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27436313
-
Niosome-Based Approach for In Situ Gene Delivery to Retina and Brain Cortex as Immune-Privileged Tissues.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Feb 25;12(3):198. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12030198. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32106545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cationic Niosomes as Non-Viral Vehicles for Nucleic Acids: Challenges and Opportunities in Gene Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Jan 22;11(2):50. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11020050. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 30678296 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual-Targeted Therapy in HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer with Trastuzumab and Novel Cholesterol-Based Nioplexes Silencing Mcl-1.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Oct 4;15(10):2424. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102424. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37896184 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of cancer stem cells and the tumor microenvironment Via NT2/D1 cells to probe pathology and treatment for cancer and beyond.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 24;16(1):605. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02158-2. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40272656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization and Synthesis of Nano-Niosomes for Encapsulation of Triacontanol by Box-Behnken Design.Molecules. 2024 Sep 18;29(18):4421. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184421. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339416 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Hyaluronic Acid Coating on the Cationic Niosomal Surface for Doxorubicin Delivery.Molecules. 2025 Mar 3;30(5):1148. doi: 10.3390/molecules30051148. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40076371 Free PMC article.
-
"Carnosine-Niosomal Delivery System for Targeted Cancer Therapy".Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun;83(2):1495-1520. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01626-w. Epub 2024 Dec 10. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39656368 Review.
References
-
- Agirre M, Ojeda E, Zarate J, et al. (2015). New insights into gene delivery to human neuronal precursor NT2 cells: a comparative study between lipoplexes, nioplexes, and polyplexes. Mol Pharm 12:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Attia N, Mashal M, Grijalvo S, et al. (2019). Cationic niosome-based hBMP7 gene transfection of neuronal precursor NT2 cells to reduce the migration of glioma cells in vitro. J Drug Delivery Sci Technol 53:101219.
-
- Attia N, Mashal M. (2020). Mesenchymal stem cells: the past present and future. In: Cell Biology and Translational Medicine, Vol. 11. Cham: Springer, 107–129. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
