Inhibition of BPHL inhibits proliferation in lung carcinoma cell lines
- PMID: 37323178
- PMCID: PMC10261862
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-23-225
Inhibition of BPHL inhibits proliferation in lung carcinoma cell lines
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is one of the most common human malignant tumors and the leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Biphenyl hydrolase-like (BPHL) is a gene encoding the human BPHL enzyme, a serine hydrolase that catalyzes the hydrolytic activation of amino acid ester prodrugs of nucleoside analogs such as valacyclovir and valganciclovir. However, the role of BPHL in lung cancer is still unknown.
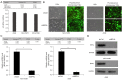
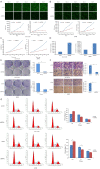
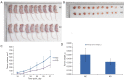
Methods: In this study, we assessed the effect BPHL knockdown on the proliferation, apoptosis, colony formation, metastasis, and cell cycle of cancer cells. BPHL knockdown NCI-H1299 and A549 cells demonstrated decreased proliferation, as measured by Celigo cell counting. The MTT assay results were consistent with Celigo cell counting. Caspase 3/7 activity increased significantly in the NCI-H1299 and A549 cells after shBPHL knockdown. Decreased colony formation in the NCI-H1299 and A54 cells after shBPHL knockdown, as measured by crystal violet staining. Transmigration assay using a Transwell demonstrated that there were significantly fewer migrating cells in the lower chamber in the BPHL knockdown NCI-H1299 and A549 cells. Cell cycle analysis by Propidium Iodide (PI) staining and fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS). We also explored the effect of BPHL knockdown on tumor growth in a mouse model of tumor implantation in nude mice.
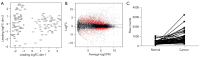
Results: We found that the knockdown of BPHL gene expression by short hairpin RNA (shRNA) leads to a decrease in proliferation, colony formation, and metastasis and an increase in apoptosis in two lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) cell lines in vitro. BPHL knockdown induces decreased tumor growth, colony formation, and metastasis; increased apoptosis; and altered cell cycle destruction. BPHL knockdown results in decreased tumor growth in vivo. Moreover, BPHL knockdown A549 cells demonstrated slower growth compared to control cells upon implantation in nude mice, confirming the in vitro findings.
Conclusions: In this study, the data indicate that BPHL potentially promotes proliferation, inhibits apoptosis, and increases colony formation and metastasis in lung cancer. Overall, our study suggests that BPHL may be a gene that promotes tumor growth in lung cancer.
Keywords: Biphenyl hydrolase-like (BPHL); inhibits proliferation; lung carcinoma cell lines.
2023 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-23-225/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Chu C, Liu BZ, Zhong L, et al. Identification of interaction between BPHL and PML-C. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2013;44:6-9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
