Clinical, biochemical and molecular characterization of Wilson's disease in Moroccan patients
- PMID: 37323222
- PMCID: PMC10267639
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2023.100984
Clinical, biochemical and molecular characterization of Wilson's disease in Moroccan patients
Abstract
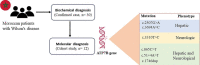
Background: Wilson Disease (WD) is an autosomal recessive inherited metabolic disease caused by mutations in the ATP7B gene. WD is characterized by heterogeneous clinical presentations expressed by hepatic and neuropsychiatric phenotypes. The disease is difficult to diagnose, and misdiagnosed cases are commonly seen.
Methods: In this study, the presented symptoms of WD, the biochemical parameters as well as its natural history are described based on cases collected in Mohammed VI Hospital University of Marrakech (Morocco). We screened and sequenced 21 exons of ATP7B gene from 12 WD patients that confirmed through biochemical diagnosis.
Results: Mutational assessment of the ATP7B gene showed six homozygous mutations in 12 individuals however, 2 patients had no evidence of any mutation in promoter and exonic regions. All mutations are pathogenic and most were missense mutations. c.2507G > A (p.G836E), c.3694A > C (p.T1232P) and c.3310 T > C (p.C1104R) that were identified in 4 patients. The other mutations were a non-sense mutation (c.865C > T (p.C1104R)) detected in 2 patients, a splice mutation (c.51 + 4A > T) detected in 2 patients and a frameshift mutation (c.1746 dup (p.E583Rfs*25) detected in 2 patients.
Conclusion: Our study is the first molecular analysis in Moroccan patients with Wilson's disease, the ATP7B mutational spectrum in the Moroccan population is diverse and still unexplored.
Keywords: ATP7B gene; Molecular genetic diagnosis; Mutations; Wilson disease.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Das S.K., Ray K. Wilson’s disease: an update. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2006;2(9):482–493. - PubMed
-
- Roelofsen H., Wolters H., Van Luyn M.J.A., Miura N., Kuipers F., Vonk R.J. Copper-induced apical trafficking of ATP7B in polarized hepatoma cells provides a mechanism for biliary copper excretion. Gastroenterology. 2000;119(3):782–793. - PubMed
-
- Roberts E.A., Schilsky M.L. Diagnosis and treatment of Wilson disease: an update. Hepatology. 2008;47(6):2089–2111. - PubMed
-
- Brunet A.-S., Marotte S., Guillaud O., Lachaux A. Familial screening in Wilson’s disease: think at the previous generation! J. Hepatol. 2012;57(6):1394–1395. - PubMed
-
- Ala A., Walker A.P., Ashkan K., Dooley J.S., Schilsky M.L. Wilson’s disease. Lancet. 2007;369(9559):397–408. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources