Characteristics of pleural effusion due to amyloidosis
- PMID: 37323369
- PMCID: PMC10263077
- DOI: 10.4103/atm.atm_433_22
Characteristics of pleural effusion due to amyloidosis
Abstract
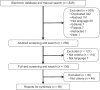
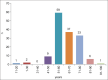
The characteristics of patients with pleural amyloidosis (PA) are poorly known. A systematic review was performed of studies reporting clinical findings, pleural fluid (PF) characteristics, and the most effective treatment of PA. Case descriptions and retrospective studies were included. The review included 95 studies with a total sample of 196 patients. The mean age was 63 years, male/female ratio was 1.6:1, and 91.9% of patients were >50 years. The most common symptom was dyspnea (88 patients). PF was generally serious (63%), predominantly lymphocytic, and with the biochemical characteristics of transudates (43.4%) or exudates (42.6%). Pleural effusion was generally bilateral (55%) and <1/3 of the hemithorax (50%), although in 21% pleural effusion (PE) exceeded 2/3. Pleural biopsy was performed in 67 patients (yield: 83.6%; 56/67) and was positive in 54% of exudates and 62.5% of unilateral effusions. Of the 251 treatments prescribed, only 31 were effective (12.4%). The combination of chemotherapy and corticosteroids was effective in 29.6% of cases, whereas talc pleurodesis was effective in 21.4% and indwelling pleural catheter in 75% of patients (only four patients). PA is more frequent in adults from 50 years of age. PF is usually bilateral, serous, and indistinctly a transudate or exudate. A pleural biopsy can aid in diagnosis if effusion is unilateral or an exudate. Treatments are rarely effective and there may be definitive therapeutic options for PE in these patients.
Keywords: Amyloidosis; pleural effusion; pleural fluid.
Copyright: © 2023 Annals of Thoracic Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lachmann HJ, Hawkins PN. Systemic amyloidosis. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006;6:214–20. - PubMed
-
- Wechalekar AD, Gillmore JD, Hawkins PN. Systemic amyloidosis. Lancet. 2016;387:2641–54. - PubMed
-
- Sipe JD, Benson MD, Buxbaum JN, Ikeda S, Merlini G, Saraiva MJ, et al. Nomenclature 2014: Amyloid fibril proteins and clinical classification of the amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2014;21:221–4. - PubMed
-
- Kyle RA, Linos A, Beard CM, Linke RP, Gertz MA, O’Fallon WM, et al. Incidence and natural history of primary systemic amyloidosis in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1950 through 1989. Blood. 1992;79:1817–22. - PubMed
-
- Berk JL. Pleural effusions in systemic amyloidosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2005;11:324–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources