Prediction of small molecule drug-miRNA associations based on GNNs and CNNs
- PMID: 37323664
- PMCID: PMC10268031
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1201934
Prediction of small molecule drug-miRNA associations based on GNNs and CNNs
Abstract
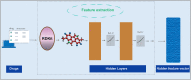
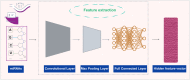
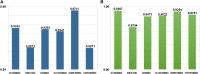
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a crucial role in various biological processes and human diseases, and are considered as therapeutic targets for small molecules (SMs). Due to the time-consuming and expensive biological experiments required to validate SM-miRNA associations, there is an urgent need to develop new computational models to predict novel SM-miRNA associations. The rapid development of end-to-end deep learning models and the introduction of ensemble learning ideas provide us with new solutions. Based on the idea of ensemble learning, we integrate graph neural networks (GNNs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to propose a miRNA and small molecule association prediction model (GCNNMMA). Firstly, we use GNNs to effectively learn the molecular structure graph data of small molecule drugs, while using CNNs to learn the sequence data of miRNAs. Secondly, since the black-box effect of deep learning models makes them difficult to analyze and interpret, we introduce attention mechanisms to address this issue. Finally, the neural attention mechanism allows the CNNs model to learn the sequence data of miRNAs to determine the weight of sub-sequences in miRNAs, and then predict the association between miRNAs and small molecule drugs. To evaluate the effectiveness of GCNNMMA, we implement two different cross-validation (CV) methods based on two different datasets. Experimental results show that the cross-validation results of GCNNMMA on both datasets are better than those of other comparison models. In a case study, Fluorouracil was found to be associated with five different miRNAs in the top 10 predicted associations, and published experimental literature confirmed that Fluorouracil is a metabolic inhibitor used to treat liver cancer, breast cancer, and other tumors. Therefore, GCNNMMA is an effective tool for mining the relationship between small molecule drugs and miRNAs relevant to diseases.
Keywords: CNN; convolutional neural networks; graph neural networks; liver cancer; miRNAs; small molecule drug.
Copyright © 2023 Niu, Gao, Xia, Zhao, Sun, Wang, Liu, Kong, Ma, Zhu, Gao, Liu, Yang, Song, Lu and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MDFGNN-SMMA: prediction of potential small molecule-miRNA associations based on multi-source data fusion and graph neural networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2025 Jan 13;26(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12859-025-06040-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 39806287 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Small Molecule-MicroRNA Associations by Sparse Learning and Heterogeneous Graph Inference.Mol Pharm. 2019 Jul 1;16(7):3157-3166. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00384. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Mol Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31136190
-
Prediction of potential small molecule-miRNA associations based on heterogeneous network representation learning.Front Genet. 2022 Dec 2;13:1079053. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1079053. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36531225 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of protein-ligand binding affinity with deep learning.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Nov 20;21:5796-5806. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.11.009. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 38213884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How the technologies behind self-driving cars, social networks, ChatGPT, and DALL-E2 are changing structural biology.Bioessays. 2025 Jan;47(1):e2400155. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400155. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 39404756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DEJKMDR: miRNA-disease association prediction method based on graph convolutional network.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 12;10:1234050. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1234050. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37780568 Free PMC article.
-
Graph attention networks for predicting drug-gene association of glucocorticoid in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A comparison with GraphSAGE.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 3;20(7):e0327619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327619. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40608705 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecules targeting microRNAs: new opportunities and challenges in precision cancer therapy.Trends Cancer. 2024 Sep;10(9):809-824. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2024.06.006. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Trends Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39107162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Graph Neural Network-Based Drug Gene Interactions of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Bone Formation.Cureus. 2024 Sep 4;16(9):e68669. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68669. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39371752 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning approaches for predicting the small molecule-miRNA associations: a comprehensive review.Mol Divers. 2025 Aug;29(4):3825-3856. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11211-9. Epub 2025 May 20. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 40392452 Review.
References
-
- Bahdanau D., Cho K., Bengio Y. (2014). "Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate.", arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0473.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

