Complete Blood Count Parameters as Prognostic Factor of Stroke: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37323954
- PMCID: PMC10262284
- DOI: 10.32598/bcn.2021.2168.2
Complete Blood Count Parameters as Prognostic Factor of Stroke: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Introduction: Stroke is known as a common cause of disability all over the world. Stroke prognosis estimation has always been a topic of interest. In this study, it was tried to investigate the prognostic value of laboratory findings of complete blood count in a systematic review.
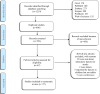
Methods: In this systematic review, literature from Medline via (PubMed, Ovid) Embase, Scopus, Cochrane Library, and ProQuest between 1988 and 2020 were included. A combination of Mesh and free terms were included in the search strategy: "Stroke", "Red Cell Distribution Width", "Blood Cell Count", "Mean corpuscular hemoglobin", and "Mean Corpuscular Volume" and with the abbreviation, in all fields. Data synthesis was achieved using content analysis.
Results: Elevated red blood cell distribution width was associated with stroke, cardiovascular events, and all-cause deaths among patients with prior stroke. Mean platelet volume has not any prognostic significance in ischemic stroke. There was a poor association between mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and stroke prognosis. Globulin and hemoglobin level predicted short-term mortality following acute ischemic stroke.
Conclusion: Complete blood count as a routine and efficient test performed in health care centers can be used to estimate the prognosis of stroke.
Keywords: Blood cell count; Erythrocyte indices; Prognosis; Stroke.
Copyright© 2022 Iranian Neuroscience Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aksoy D., Inanir A., Ayan M., Cevik B., Kurt S., Ünaldi H. K. (2013). Predictors of mortality and morbidity in acute ischemic stroke. Arch Neuropsychiatry, 50(50), 40–44. [DOI:10.4274/Npa.y6287] - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources