Post-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic tool in patients treated with tocilizumab for severe COVID-19 pneumonia - a single center experience
- PMID: 37324114
- PMCID: PMC10231768
- DOI: 10.11613/BM.2023.020704
Post-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic tool in patients treated with tocilizumab for severe COVID-19 pneumonia - a single center experience
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Post-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic tool in patients treated with tocilizumab for severe COVID-19 pneumonia - a single center experience.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2023 Oct 15;33(3):031201. doi: 10.11613/BM.2023.031201. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2023. PMID: 37841774 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Tocilizumab is used in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia and high concentration of IL-6. We studied potential prognostic role of neutrophil and lymphocyte count regarding tocilizumab treatment.
Materials and methods: We enrolled 31 patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia and higher serum IL-6 concentration. The samples were taken on the day of tocilizumab administration and five days later. We used ROC analysis to investigate the association between the analysed parameters and 30-day mortality in order to determine the best pre-treatment and post-treatment prognostic factor. Kaplan-Meier curves and log-rank test were used to present and to analyse the difference in survival.
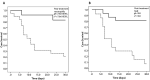
Results: Patients had a median age of 63 (55-67) years and were treated with a median tocilizumab dose of 800 mg. During the 30-day follow-up period, 17 patients died (30-day mortality 54%). Among pre-treatment variables, neutrophil count had the best prognostic accuracy (AUC 0.81, 95%CI: 0.65-0.96, P = 0.004), while neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) had the highest accuracy among post-treatment variables in predicting 30-day mortality (AUC 0.94, 95%CI: 0.86-1.00, P < 0.001). Among post-treatment parameters, neutrophil count and NLR were equally good prognostic factors. Post-treatment NLR cut-off of 9.8 had the sensitivity of 81% and specificity of 93%. Patients with NLR ≥ 9.8 had the median survival of 7.0 (3-10) days vs. median survival not reached in patients with NLR < 9.8 (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Pre-treatment and post-treatment neutrophil count with post-treatment NLR may represent prognostic tools for patients with higher IL-6 concentration in severe COVID-19 pneumonia treated with tocilizumab.
Keywords: COVID-19; interleukin-6; lymphocytes; neutrophils; tocilizumab.
Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest None declared.