Integration of nurse-led virtual reviews with growth hormone device-linked patient adherence information: a mixed methods feasibility study
- PMID: 37324260
- PMCID: PMC10266208
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1167854
Integration of nurse-led virtual reviews with growth hormone device-linked patient adherence information: a mixed methods feasibility study
Abstract
Introduction: Easypod-connect™ for childhood growth disorders is a unique connected system that enables transmission of injection adherence information for recombinant human growth hormone (r-hGH). Although this system has the potential to facilitate greater adherence, observational studies have shown declining adherence over prolonged periods when used without additional support. Supplemental nurse practitioner support has been envisaged but not investigated; in this study, we have undertaken feasibility analysis of nurse-led virtual reviews (NVR) in combination with easypod-connect™ in a single centre using quantitative and qualitative analyses.
Aims: We aimed to test feasibility by assessing compliance with NVR, height standard deviation score (SDS) gain, adherence improvement and patient opinions.
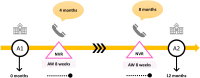
Methods: Patients using easypod™ r-hGH were recruited prospectively to a 12-month study with two telephone NVR appointments in addition to standard of care in-person hospital outpatient visits. A subset was recruited for a semi-structured interview for qualitative thematic analysis.
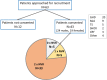
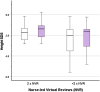
Results: Forty-three patients of median (range) age 10.7 (6.7, 15.2) were recruited for a period of 1.1 (0.7, 1.8) years. Thirty-three (76.7%) patients were fully compliant with NVR integration with easypod-connect™, establishing feasibility. Median (inter-quartile range, IQR) height SDS improved from -1.85 (-2.44, -1.37) to -1.48 (-2.14, -1.07) (p<0.001) while adherence remained similar in the majority from study start [96.5 (88.8, 100.0)] to end [99.0 (94.0, 100.0)]. Qualitative analysis identified themes supporting patient benefit: practicalities of appointments, perceived purpose and significance of virtual reviews, and the importance of optimising growth. Four patients complained of injection pain, of whom two switched to an alternative r-hGH device.
Conclusion: Our study has demonstrated the feasibility of nurse-led virtual review integration with easypod-connect™ in a mixed methods study, laying the foundation for research in larger groups over longer periods. Nurse practitioner supported application of easypod-connect™ offers the potential for improved growth outcomes in all r-hGH devices providing adherence information.
Keywords: adherence; children; growth hormone; growth hormone device; nurse-led; short stature.
Copyright © 2023 Stokes, Jones, Worth, Nicholson, Fullwood and Banerjee.
Conflict of interest statement
IB is the Associate Medical Director for Research and Innovation at the Royal Manchester Children’s Hospital and is on the advisory boards of NICE Head Injury guidelines, Pituitary Foundation, Living with CAH, Congenital Hyperinsulinism Charity UK and Congenital Hyperinsulinism International Committee. He is the Chair of the European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology Communications Committee, Chair of NIHR British Society of Paediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes BSPED Clinical Studies Group and Treasurer, Manchester Medical Society. IB has received grant support from Merck, Zealand Pharma, Crinetics and Dexcom, and honoraria from Merck advisory board and project design. He does not own direct shares or equities in Merck, Zealand Pharma, Crinetics or Dexcom. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adherence to treatment in children with growth hormone deficiency, small for gestational age and Turner syndrome in Mexico: results of the Easypod™ connect observational study (ECOS).J Endocrinol Invest. 2020 Oct;43(10):1447-1452. doi: 10.1007/s40618-020-01218-4. Epub 2020 Apr 1. J Endocrinol Invest. 2020. PMID: 32239476 Free PMC article.
-
Adherence in children with growth hormone deficiency treated with r-hGH and the easypod™ device.J Endocrinol Invest. 2016 Dec;39(12):1419-1424. doi: 10.1007/s40618-016-0510-0. Epub 2016 Jul 12. J Endocrinol Invest. 2016. PMID: 27406716 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of treatment adherence with growth hormone by easypod™ device: experience of an Italian centre.Ital J Pediatr. 2018 Sep 27;44(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13052-018-0548-z. Ital J Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 30261918 Free PMC article.
-
Adherence to r-hGH Therapy in Pediatric Growth Hormone Deficiency: Current Perspectives on How Patient-Generated Data Will Transform r-hGH Treatment Towards Integrated Care.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2022 Jul 11;16:1663-1671. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S271453. eCollection 2022. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2022. PMID: 35846871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Easypod: a new electronic injection device for growth hormone.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2008 May;5(3):297-304. doi: 10.1586/17434440.5.3.297. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2008. PMID: 18452378 Review.
References
-
- Gomez R, Ahmed SF, Maghnie M, Li D, Tanaka T, Miller BS. Treatment adherence to injectable treatments in pediatric growth hormone deficiency compared with injectable treatments in other chronic pediatric conditions: a systematic literature review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) (2022) 13:95224. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.795224 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Landsberger HA, Roethlisberger FJ, I. New York State School of and R. Labor . Hawthorne Revisited : management and the worker: its critics, and developments in human relations in industry. New York: Cornell University: (1958).
-
- Michie S, Johnston M, Francis J, Hardeman W, Eccles M. From theory to intervention: mapping theoretically derived behavioural determinants to behaviour change techniques. Appl Psychol (2008) 57:660–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-0597.2008.00341.x - DOI
-
- Fogg BJ. Persuasive computing : technologies designed to change attitudes and behaviors. Burlington: Morgan Kaufmann; (2003).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

