Patient decision aids for patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma: development process and alpha and beta testing
- PMID: 37324263
- PMCID: PMC10264809
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1162537
Patient decision aids for patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma: development process and alpha and beta testing
Abstract
Background: Patient decision aids (PtDAs) are structured clinical tools that facilitate shared decision-making. Two important treatment decisions for patients with differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC), which could benefit from PtDAs, are as follows (1): the extent of surgery decision in patients with low-risk DTC and (2) the decision to start or delay starting the treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in patients with advanced tumors.
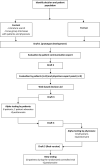
Material and methods: PtDAs for these two decisions were developed using the International Patient Decision Aids Standards (IPDAS) quality criteria in an iterative process of prototype development via alpha and beta testing by patients and physicians. The information content of the PtDAs was based on the available literature, current guidelines, and patient's needs, preferences, and values.
Results: The web-based PtDAs underwent two rounds of alpha testing, revisions, and beta testing. The PtDAs have the same structure, consisting of six steps: a general introduction, information about the treatment options, comparing the treatment options, knowledge questions, a values clarification exercise, and saving the information. The alpha testing (n = 8 patients, n = 10 physicians) showed that the PtDAs were highly acceptable and usable for decision-making. Results of the beta testing in 20 patients showed that two patients did not use the PtDA; the other 18 patients found that the PtDAs were readable (n = 17) and helpful (n = 14) for decision-making. All patients recommend using the PtDAs.
Conclusions: Evidence-based PtDAs were created for patients with DTC for two different treatment decisions. Our final version was judged to be clear, balanced, and helpful in decision-making.
Keywords: decision aid; shared decision making; surgery; thyroid cancer; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Copyright © 2023 Koot, Hermens, Ottevanger, Netea-Maier, Stalmeier and the COMBO study group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kidney disease pathways, options and decisions: an environmental scan of international patient decision aids.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020 Dec 4;35(12):2072-2082. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa102. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32830240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of an online patient decision aid for kidney failure treatment modality decisions.BMC Nephrol. 2022 Jul 6;23(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-02853-0. BMC Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35794539 Free PMC article.
-
How Inclusive Are Patient Decision Aids for People with Limited Health Literacy? An Analysis of Understandability Criteria and the Communication about Options and Probabilities.Med Decis Making. 2025 Feb;45(2):143-155. doi: 10.1177/0272989X241302288. Epub 2024 Dec 14. Med Decis Making. 2025. PMID: 39673417 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Patient Decision Aid Attributes on Patient Outcomes: A Network Meta-Analysis of a Systematic Review.Med Decis Making. 2025 May;45(4):437-448. doi: 10.1177/0272989X251318640. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Med Decis Making. 2025. PMID: 39968925 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a web-based patient decision aid for initiating disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs using user-centred design methods.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2017 Apr 26;17(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12911-017-0433-5. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2017. PMID: 28441950 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Implementing active surveillance for low-risk thyroid carcinoma into clinical practice: collaborative recommendations for Latin America.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Jun 3;68:e230371. doi: 10.20945/2359-4292-2023-0371. eCollection 2024. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 39420909 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oncoline . Schildkliercarcinoom. (2015). Available at: https://richtlijnendatabase.nl/richtlijn/schildkliercarcinoom/algemeen.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical