Traditional Chinese medicine use is associated with lower risk of pneumonia in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a population-based retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 37324478
- PMCID: PMC10267408
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1185809
Traditional Chinese medicine use is associated with lower risk of pneumonia in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a population-based retrospective cohort study
Abstract
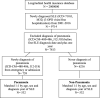
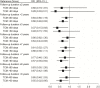
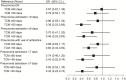
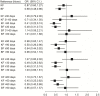
Objectives: To investigate the association between traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) therapy and the risk of pneumonia in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Methods: This population-based control study analyzed the data retrieved from the National Health Insurance Research database in Taiwan. From a cohort of 2 million records of the 2000-2018 period, 9,714 newly diagnosed patients with SLE were initially included. 532 patients with pneumonia and 532 patients without pneumonia were matched 1:1 based on age, sex, and year of SLE diagnosis using propensity score matching. The use of TCM therapy was considered from the SLE diagnosis date to the index date and the cumulative days of TCM therapy were used to calculate the dose effect. Conditional logistic regression was used to investigate the risk of pneumonia infection. Furthermore, to explore the severity of pneumonia in SLE, sensitivity analyses were performed after stratification using the parameters of emergency room visit, admission time, and antibiotic use. Results: TCM therapy for >60 days could significantly reduce the risk of pneumonia in patients with SLE (95% CI = 0.46-0.91; p = 0.012). Stratified analysis showed that TCM use also reduced the risk of pneumonia in younger and female patients with SLE by 34% and 35%, respectively. TCM for >60 days significantly reduced the risk of pneumonia in the follow-up periods of >2, >3, >7, and >8 years. In addition, the exposure of TCM for >60 days reduced the risk of pneumonia in patients with SLE who were treated with antibiotics for moderate or severe pneumonia. Finally, the study found that using formulae to tonify the kidney for more than 90 days and formulae to activate blood circulation for less than 30 days could significantly reduce the risk of pneumonia infection in patients with SLE. Conclusion: TCM use is associated with a lower risk of pneumonia among patients with SLE.
Keywords: cohort; infection; pneumonia; systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE); traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Wang, Yang, Ye, Wang and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Traditional Chinese medicine in synergy with conventional therapy improves renal outcomes and provides survival benefit in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a cohort study from the largest health care system in Taiwan.Curr Med Res Opin. 2025 Mar;41(3):559-567. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2025.2478160. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Curr Med Res Opin. 2025. PMID: 40079084
-
Traditional Chinese medicine therapy improves the survival of systemic lupus erythematosus patients.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016 Apr;45(5):596-603. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.09.006. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016. PMID: 26522135
-
Traditional Chinese medicine therapy decreases the pneumonia risk in patients with dementia.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Sep;95(37):e4917. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004917. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27631269 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Therapy Combining Chinese Herbal Medicines With Conventional Treatment Reduces the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Among Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Retrospective Population-Based Cohort Study.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 27;12:737105. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.737105. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34646137 Free PMC article.
-
Mycoplasma pneumonia Infection Is Associated With an Increased Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Nationwide, Retrospective Cohort Study.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 21;13:815136. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.815136. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35531287 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Mechanism of Chinese Medicine in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Narrative Review.Chin J Integr Med. 2025 Feb;31(2):157-169. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3762-0. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Chin J Integr Med. 2025. PMID: 39240290 Review.
-
Quality Assessment of Cohort Studies in Complementary and Alternative Medicine: A Scoping Review Over Two Decades.Iran J Public Health. 2025 Jan;54(1):74-87. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v54i1.17576. Iran J Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39902362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal and survival benefits of seventeen prescribed Chinese herbal medicines against oxidative-inflammatory stress in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with chronic kidney disease: a real-world longitudinal study.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 3;14:1309582. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1309582. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38235107 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

