Therapeutic management of atypical antipsychotic‑related metabolic dysfunctions using GLP‑1 receptor agonists: A systematic review
- PMID: 37324512
- PMCID: PMC10265718
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2023.12054
Therapeutic management of atypical antipsychotic‑related metabolic dysfunctions using GLP‑1 receptor agonists: A systematic review
Abstract
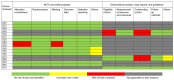
Metabolic disorders (MDs) like obesity, dyslipidemia, and type 2 diabetes are more frequently observed in patients diagnosed with psychiatric disorders undergoing treatment with antipsychotics, particularly atypical agents, than in the general population. The second generation of antidiabetics (SGAD) has been associated with cardiovascular benefits in large clinical trials which represent an important advantage over first-generation agents and might be of interest in the psychiatric population where multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease (e.g., smoking, lack of exercise, and lack of healthy diet) are common occurrences. Therefore, this systematic review focused on the evaluation of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs), as a representative of the SGAD, to determine whether these agents may be recommended in patients with psychiatric disorders and MDs. For analysis, three electronic databases and clinical trial registers were explored for papers published between January 2000 and November 2022. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 20 clinical and preclinical trials, therapeutic guidelines, and meta-analyses were reviewed, and clinical recommendations were formulated. The large majority of the reviewed data (nine papers) were graded 'moderate' based on the GRADE criteria. The efficacy and tolerability of liraglutide and exenatide in the management of antipsychotic-induced MDs were supported by evidence of average quality, while the results regarding other GLP-1RAs were not sufficient to formulate a recommendation for their administration in this specific population. Clozapine and olanzapine had the most negative consequences on body weight, glycemic, and lipid metabolism. Therefore, careful monitoring of metabolic parameters is required when these are prescribed. Liraglutide and exenatide may be recommended as augmentative agents to metformin therapy, especially in patients receiving these two atypical antipsychotics, but most of the reviewed data supported the efficacy of GLP-1RAs only during the treatment administration. The two follow-up studies retrieved in the literature reported modest effects after GLP-1RA discontinuation after 1 year; therefore, long-term monitoring of metabolic parameters is required. More research is needed, and three randomized clinical trials are already ongoing, to evaluate the effects of GLP-1RAs in decreasing body weight, but also on other important metabolic variables, such as HbA1c status, fasting glucose levels, and lipid levels in patients receiving antipsychotic treatment.
Keywords: GLP-1 receptor agonists; atypical antipsychotics; obesity; oral antidiabetics; schizophrenia spectrum disorders; type 2 diabetes; weight gain.
Copyright: © Vasiliu.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Chang CK, Hayes RD, Perera G, Broadbent MT, Fernandes AC, Lee WE, Hotopf M, Stewart R. Life expectancy at birth for people with serious mental illness and other major disorders from a secondary mental health care case register in London. PLoS One. 2011;6(e19590) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019590. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vasiliu O, Vasile D, Făinărea AF, Pătrașcu MC, Morariu EA, Manolache R, Alexandru I, Androne FT. Analysis of risk factors for antipsychotic-resistant schizophrenia in young patients-a retrospective analysis. Rom J Mil Med. 2018;(CXXI):25–29.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous