Quality evaluation of compounds in leaves of six Taxus species based on UPLC-MS/MS and chemometrics
- PMID: 37324558
- PMCID: PMC10264637
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1193188
Quality evaluation of compounds in leaves of six Taxus species based on UPLC-MS/MS and chemometrics
Abstract
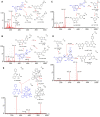
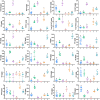
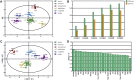
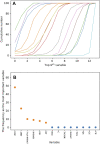
Introduction: Taxus species are used as medicinal plants all over the world. The leaves of Taxus species are sustainable medicinal resources that are rich in taxoids and flavonoids. However, traditional identification methods cannot effectively identify Taxus species on the basis of leaces used as raw medicinal materials, because their appearance and morphological characteristics are almost the same, and the probability of error identification increases in accordance with the subjective consciousness of the experimenter. Moreover, although the leaves of different Taxus species have been widely used, their chemical components are similar and lack systematic comparative research. Such a situation is challenging for quality assessment. Materials and methods: In this study, ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry combined with chemometrics was applied for the simultaneous determination of eight taxoids, four flavanols, five flavonols, two dihydroflavones, and five biflavones in the leaves of six Taxus species, namely, T. mairei, T. chinensis, T. yunnanensis, T. wallichiana, T. cuspidata, and T. media. Chemometric methods, including hierarchical cluster analysis, principal component analysis, orthogonal partial least squares-discriminate analysis, random forest iterative modeling, and fisher linear discriminant analysis, were utilized to differentiate and evaluate the six Taxus species. Results: This proposed method exhibited good linearity (R 2 = 0.9999-0.9972) with a lower quantification limits of 0.94-3.05 ng/mL for all analytes. The intra- and inter-day precisions were within 6.83%. Six compounds, namely, 7-xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol, ginkgetin, rutin, aromadendrin, 10-deacetyl baccatin III, and epigallocatechin, were identified through chemometrics for the first time. These compounds can be used as important chemical markers to distinguish the above six Taxus species rapidly. Conclusion: This study established a method for determination of the leaves of six Taxus species, and revealing the differences in the chemical components of these six Taxus species.
Keywords: Taxus species; chemometrics; flavonoids; quality control; taxoids.
Copyright © 2023 Cai, Song, Jiang, Lin, Zhang, Zhang, Lin, Huang, Xue, Huang, Xu, Xu and Yam.
Conflict of interest statement
Author QX was employed by Fujian South Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Simultaneous determination of taxoids and flavonoids in twigs and leaves of three Taxus species by UHPLC-MS/MS.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020 Sep 10;189:113456. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113456. Epub 2020 Jul 2. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020. PMID: 32653816
-
Simultaneous determination of seven taxoids in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS and pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Taxus yunnanensis extracts.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015 Mar 25;107:346-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Jan 10. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015. PMID: 25645339
-
Metabolic Variations of Flavonoids in Leaves of T. media and T. mairei Obtained by UPLC-ESI-MS/MS.Molecules. 2019 Sep 12;24(18):3323. doi: 10.3390/molecules24183323. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31547329 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal Dynamics of Metabolites in Needles of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei.Molecules. 2016 Oct 20;21(10):1403. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101403. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27775631 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of paclitaxel and other six taxoids in Taxus species by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2009 Jan 15;49(1):81-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2008.10.006. Epub 2008 Oct 19. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2009. PMID: 19036549
Cited by
-
Mass Spectrometry-Imaging Analysis of Active Ingredients in the Leaves of Taxus cuspidata.ACS Omega. 2024 Apr 10;9(16):18634-18642. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c01440. eCollection 2024 Apr 23. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38680336 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the Medicinal Chemistry and Pharmacology of Taxus × media.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 25;25(11):5756. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115756. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Deep Dive into the Botanical and Medicinal Heritage of Taxus.Plants (Basel). 2025 May 11;14(10):1439. doi: 10.3390/plants14101439. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40431004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cui H.-C., Zheng W.-H., Fu Y.-F., Li X.-Y., Fu Y.-J., Gu C.-B. (2022). Determination and analysis of seven Taxanes in different Taxus species by HPLC method. For. Eng. 38 (4), 118–124. 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8023.2022.04.015 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

