Effects of sugarcane variety and nitrogen application level on the quality and aerobic stability of sugarcane tops silage
- PMID: 37324669
- PMCID: PMC10262686
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1148884
Effects of sugarcane variety and nitrogen application level on the quality and aerobic stability of sugarcane tops silage
Abstract
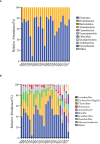
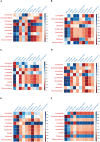
To better understand the effects of sugarcane variety and nitrogen application level on silage, we analyzed the fermentation quality, microbial community dynamics, and aerobic exposure of sugarcane tops silage from three sugarcane varieties (B9, C22, and T11) treated with three levels of nitrogen (0, 150, and 300 kg/ha urea). After 132 days of silage, the sugarcane tops silage produced from variety B9, with strong nitrogen fixation ability, treated with nitrogen had the highest crude protein (CP) contents, pH, and yeast counts (P < 0.05), as well as the lowest Clostridium counts (P < 0.05), and the CP increased with increasing N application level (P < 0.05). In contrast, the sugarcane tops silage produced from variety C22, with poor nitrogen fixation ability, treated with 150 kg/ha nitrogen had the highest lactic acid bacteria (LAB) counts, dry matter (DM), organic matter (OM) and lactic acid (LA) contents (P < 0.05), as well as the lowest acid detergent fiber (ADF) and neutral detergent fiber (NDF) contents (P < 0.05). However, these results were not present in the sugarcane tops silage produced from variety T11, with no nitrogen fixation ability, whether it was treated with nitrogen or not; although the silage was treated with 300 kg/ha nitrogen, the ammonia-N (AN) content was the lowest (P < 0.05). After 14 days of aerobic exposure, Bacillus abundance increased in the sugarcane tops silage produced from variety C22 treated with 150 kg/ha nitrogen and from varieties C22 and B9 treated with 300 kg/ha nitrogen, while Monascus abundance increased in the sugarcane tops silage produced from varieties B9 and C22 treated with 300 kg/ha nitrogen and from variety B9 treated with 150 kg/ha nitrogen. However, correlation analysis showed that Monascus was positively correlated with Bacillus irrespective of nitrogen level and sugarcane variety. Our results indicated that sugarcane variety C22, with poor nitrogen fixation ability, treated with 150 kg/ha nitrogen produced the highest sugarcane tops silage quality and inhibited the proliferation of harmful microorganisms during spoilage.
Keywords: N-fixing abilities; bacterial community; fermentation quality; fungal community; nitrogen fertilizer; sugarcane tops.
Copyright © 2023 Gu, Zhang, Zhou, Lin and Zou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects and function of citric acid on fermentation quality and microbial community in sugarcane tops silage with high and low water-soluble carbohydrate content.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jan 23;25(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06063-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39849361 Free PMC article.
-
Community of natural lactic acid bacteria and silage fermentation of corn stover and sugarcane tops in Africa.Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2020 Aug;33(8):1252-1264. doi: 10.5713/ajas.19.0348. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32054211 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ferulic acid esterase-producing Lactobacillus fermentum and cellulase additives on the fermentation quality and microbial community of alfalfa silage.PeerJ. 2019 Oct 8;7:e7712. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7712. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31608168 Free PMC article.
-
Silage preparation and fermentation quality of kudzu, sugarcane top and their mixture treated with lactic acid bacteria, molasses and cellulase.Anim Sci J. 2017 Nov;88(11):1715-1721. doi: 10.1111/asj.12840. Epub 2017 May 30. Anim Sci J. 2017. PMID: 28560744
-
Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives.J Dairy Sci. 2018 May;101(5):3980-4000. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13839. J Dairy Sci. 2018. PMID: 29685273 Review.
Cited by
-
Promotional Properties of ACC Deaminase-Producing Bacterial Strain DY1-3 and Its Enhancement of Maize Resistance to Salt and Drought Stresses.Microorganisms. 2023 Oct 28;11(11):2654. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112654. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38004666 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and function of citric acid on fermentation quality and microbial community in sugarcane tops silage with high and low water-soluble carbohydrate content.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jan 23;25(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06063-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39849361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbasi D., Rouzbehan Y., Rezaei J. (2012). Effect of harvest date and nitrogen fertilization rate on the nutritive value of amaranth forage (Amaranthus hypochondriacus). Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 171, 6–13. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2011.09.014 - DOI
-
- Ali N., Wang S. R., Zhao J., Dong Z. H., Li J. F., Nazar M., et al. . (2020). Microbial diversity and fermentation profile of red clover silage inoculated with reconstituted indigenous and exogenous epiphytic microbiota. Bioresour. Technol. 314, 123606. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123606 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Assouma S. M. S. O. O., Çelen A. E. (2022). Effects of different nitrogen doses and cultivars on some nutritive value of annual ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum var. westerwoldicum) silage. Ege Üniversitesi Ziraat Fakültesi Dergisi. 59, 225–234. doi: 10.20289/zfdergi.970316 - DOI
-
- Bai J., Xu D., Xie D., Wang M., Li Z., Guo X. (2020). Effects of antibacterial peptide-producing Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus buchneri on fermentation, aerobic stability, and microbial community of alfalfa silage. Bioresour. Technol. 315, 123881. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123881 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ball D. M., Hovelend C. S., Lacefield G. D. (1996). Forage quality in southern forages (Norcross, Georgia: Potash & Phosphate Institute; ), p:124–p:132.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

