Mulberry extract upregulates cholesterol efflux and inhibits p38 MAPK-NLRP3-mediated inflammation in foam cells
- PMID: 37324843
- PMCID: PMC10261774
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3296
Mulberry extract upregulates cholesterol efflux and inhibits p38 MAPK-NLRP3-mediated inflammation in foam cells
Abstract
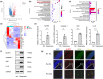
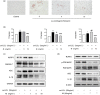
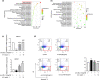
The accumulation of foam cells in arterial intima and the accompanied chronic inflammation are considered major causes of neoatherosclerosis and restenosis. However, both the underlying mechanism and effective treatment for the disease are yet to be uncovered. In this study, we combined transcriptome profiling of restenosis artery tissue and bioinformatic analysis to reveal that NLRP3 inflammasome is markedly upregulated in restenosis and that several restenosis-related DEGs are also targets of mulberry extract, a natural dietary supplement used in traditional Chinese medicine. We demonstrated that mulberry extract suppresses the formation of ox-LDL-induced foam cells, possibly by upregulating the cholesterol efflux genes ABCA1 and ABCG1 to inhibit intracellular lipid accumulation. In addition, mulberry extract dampens NLRP3 inflammasome activation by stressing the MAPK signaling pathway. These findings unveil the therapeutic value of mulberry extract in neoatherosclerosis and restenosis treatment by regulating lipid metabolism and inflammatory response of foam cells.
Keywords: MAPK signaling pathway; NLRP3 inflammasome; foam cells; mulberry; restenosis.
© 2023 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome attenuates foam cell formation of THP-1 macrophages by suppressing ox-LDL uptake and promoting cholesterol efflux.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jan 1;495(1):382-387. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.025. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29122594
-
Inflammatory corpuscle AIM2 facilitates macrophage foam cell formation by inhibiting cholesterol efflux protein ABCA1.Sci Rep. 2024 May 11;14(1):10782. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61495-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38734775 Free PMC article.
-
Diterpenoids inhibit ox-LDL-induced foam cell formation in RAW264.7 cells by promoting ABCA1 mediated cholesterol efflux.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 12;14:1066758. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1066758. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36713845 Free PMC article.
-
Gypenoside XVII inhibits ox-LDL-induced macrophage inflammatory responses and promotes cholesterol efflux through activating the miR-182-5p/HDAC9 signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 30;319(Pt 1):117070. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117070. Epub 2023 Aug 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37625608
-
ABC Transporters, Cholesterol Efflux, and Implications for Cardiovascular Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1276:67-83. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-6082-8_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32705595 Review.
Cited by
-
SGLT2 inhibitor improves the prognosis of patients with coronary heart disease and prevents in-stent restenosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jan 11;10:1280547. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1280547. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38274313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mulberry and Hippophae-based solid beverage attenuate hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis via adipose tissue-liver axis.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Apr 8;12(7):5052-5064. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4155. eCollection 2024 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39055214 Free PMC article.
-
p-Coumaric acid modulates cholesterol efflux and lipid accumulation and inflammation in foam cells.Nutr Res Pract. 2024 Dec;18(6):774-792. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2024.18.6.774. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Nutr Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39651322 Free PMC article.
-
Mulberry MnGolS2 Mediates Resistance to Botrytis cinerea on Transgenic Plants.Genes (Basel). 2023 Oct 6;14(10):1912. doi: 10.3390/genes14101912. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895261 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Role and Mechanism of Mulberry Extract in Immune Modulation: Focus on Chemical Compositions, Mechanistic Insights, and Extraction Techniques.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 14;25(10):5333. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105333. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791372 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agostini, L. , Martinon, F. , Burns, K. , McDermott, M. F. , Hawkins, P. N. , & Tschopp, J. (2004). NALP3 forms an IL‐1beta‐processing inflammasome with increased activity in Muckle‐Wells autoinflammatory disorder. Immunity, 20, 319–325. - PubMed
-
- Funk, J. L. , Feingold, K. R. , Moser, A. H. , & Grunfeld, C. (1993). Lipopolysaccharide stimulation of RAW 264.7 macrophages induces lipid accumulation and foam cell formation. Atherosclerosis, 98, 67–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

