Mycotoxins in milk: Occurrence and evaluation of certain detoxification attempts
- PMID: 37324856
- PMCID: PMC10261776
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3254
Mycotoxins in milk: Occurrence and evaluation of certain detoxification attempts
Abstract
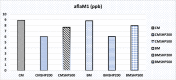
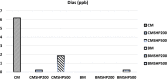
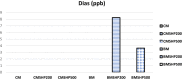
Milk contaminated with mycotoxins is a significant issue affecting human health, especially in infants. The current study aimed to investigate the presence of mycotoxins in milk collected from women farmers' vendors (WFV), and to evaluate certain herbal plant fibers as green mycotoxin binders. Moreover, explore the binding efficiency ratios of mycotoxins using shaking or soaking process incorporated with herbal extracts. Furthermore, compare the taste evaluations of tested milk are enriched with herbal extracts. Results indicated that the fumonisins were not detected in the collected cow milk samples but realized a 25% occurrence ratio in buffalo's milk samples. A high occurrence ratio of aflatoxin M1 (aflaM1) was observed in buffalo and cow milk samples. The soaking process of plant fibers in contaminated milk overnight significantly degrades and adsorbs mycotoxins particles. The shacking process incorporated with plant fibers exhibited more effectiveness in mycotoxins degradation than soaking or shacking processes alone. The speed of shacking process played an important role in the mycotoxin's binding process. All the tested plant fibers effectively reduced all mycotoxin presence in contaminated milk, especially green tea, during the soaking or shacking process. Moreover, the shacking process incorporated with plant fibers promoted and supported the mycotoxins degradation process.
Keywords: milk; mycotoxins; plant fibers bio‐binders; shacking; soaking.
© 2023 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Abd El‐Hack, M. E. , Elnesr, S. S. , Alagawany, M. , Gado, A. , Noreldin, A. E. , & Gabr, A. A. (2020). Impact of green tea (Camellia sinensis) and epigallocatechin gallate on poultry. World's Poultry Science Journal, 76(1), 49–63.
-
- Abdelnaby, A. , Abdelaleem, N. M. , Elshewy, E. , Mansour, A. H. , & Ibrahim, S. (2022). The efficacy of clay bentonite, date pit, and chitosan nanoparticles in the detoxification of aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A from milk. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 20305–20317. 10.1007/s11356-021-17254-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abdelnour, S. A. , Swelum, A. A. , Salama, A. , Al‐Ghadi, M. Q. , Qattan, S. Y. , Abd El‐Hack, M. E. , & El‐Saadony, M. T. (2020). The beneficial impacts of dietary phycocyanin supplementation on growing rabbits under high ambient temperature. Italian Journal of Animal Science, 19(1), 1046–1056.
-
- Aboshora, W. , Lianfu, Z. , Dahir, M. , Gasmalla, M. A. , Musa, A. , Omer, E. , & Thapa, M. (2014). Physicochemical, nutritional and functional properties of the epicarp, flesh and pitted sample of doum fruit (Hyphaene thebaica). Journal of Food and Nutrition Research, 2, 180–186.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

