Sika deer velvet antler protein extract modulater bone metabolism and the structure of gut microbiota in ovariectomized mice
- PMID: 37324858
- PMCID: PMC10261755
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3316
Sika deer velvet antler protein extract modulater bone metabolism and the structure of gut microbiota in ovariectomized mice
Abstract
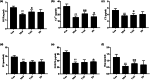
Osteoporosis is a systemic osteopathy characterized by bone metabolism disorders that become more serious with age increases in postmenopausal women. Recent studies have found that antler protein is the main bioactive component of cervus pantotrichum, and it has a positive regulatory effect on bone metabolism and can improve estrogen level. This study aimed to investigate the effect of velvet antler extract (VAE) on the prevention of osteoporosis and the modulation of gut microbiota in ovariectomized (OVX) mice. OVX mice treated with 12 weeks of VAE exhibited higher levels of serum BGP, Ca2+, CT, and HyP (p < .05). Micro-CT scans showed that VAE significantly elevated bone volume fraction (BV/TV), trabecular bone number (Tb.N), trabecular bone thickness (Tb.Th), trabecular bone connection density (Conn.D), decreased trabecular separation (Tb.Sp), and structural modality index (SMI) than untreated OVX mice. The right tibial retinaculum in the VAE group was clearer, with a clearer reticular structure, smaller gaps, a tighter distribution, and a more orderly arrangement. The gut microbiota of the cecal contents was analyzed by 16 s rDNA amplicon sequencing. The data indicated that VAE modulated the species, numbers, and diversity of the gut microbiota in OVX mice. Ovariectomy caused dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota by increasing the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes in mice, but the ratio decreased after treatment with VAE. These results suggest that VAE has a therapeutic effect on OVX mice via modulate bone-related biochemical markers in serum and structure of gut microbiota.
Keywords: OVX mice; gut microbiota; osteoporosis; protein extract; sika deer velvet antler.
© 2023 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non‐financial interests to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Kefir Peptides Prevent Estrogen Deficiency-Induced Bone Loss and Modulate the Structure of the Gut Microbiota in Ovariectomized Mice.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 9;12(11):3432. doi: 10.3390/nu12113432. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33182364 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of chemical compositions and osteoprotective effects of different sections of velvet antler.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):352-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.10.060. Epub 2013 Nov 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24212078
-
[Moxibustion Inhibits Postmenopausal Bone Loss by Regulating the Metabolism of Gut Microbiota-Related Serotonin].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Jan 20;56(1):129-136. doi: 10.12182/20250160604. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40109464 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Irisin mitigates osteoporotic-associated bone loss and gut dysbiosis in ovariectomized mice by modulating microbiota, metabolites, and intestinal barrier integrity.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Apr 16;26(1):374. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08622-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40241040 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of periodontitis on bone and tryptophan metabolism of gut microbiota in estrogen-deficient mice].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Apr 9;59(4):354-363. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112144-20231225-00307. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38548592 Chinese.
Cited by
-
The Role of Herbal Medicine in Modulating Bone Homeostasis.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(7):634-643. doi: 10.2174/0115680266286931240201131724. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38333981 Review.
-
Asperuloside alleviates osteoporosis by promoting autophagy and regulating Nrf2 activation.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Dec 19;19(1):855. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05320-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39702357 Free PMC article.
-
From gut to bone: deciphering the impact of gut microbiota on osteoporosis pathogenesis and management.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 25;14:1416739. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1416739. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39386168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterizing therapeutic effects of velvet antler using different omics strategies.J Tradit Complement Med. 2024 Aug 13;15(3):229-236. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2024.08.002. eCollection 2025 May. J Tradit Complement Med. 2024. PMID: 40486283 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Black, D. M. , Reid, I. R. , Cauley, J. A. , Cosman, F. , Leung, P. C. , Lakatos, P. , Lippuner, K. , Cummings, S. R. , Hue, T. F. , Mukhopadhyay, A. , Tan, M. , Aftring, R. P. , & Eastell, R. (2015). The effect of 6 versus 9 years of zoledronic acid treatment in osteoporosis: A randomized second extension to the HORIZON‐pivotal fracture trial (PFT). Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 30(5), 934–944. 10.1002/jbmr.2442 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

