Isolation and antioxidant characterization of theaflavin for neuroprotective effect in mice model
- PMID: 37324903
- PMCID: PMC10261812
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3337
Isolation and antioxidant characterization of theaflavin for neuroprotective effect in mice model
Abstract
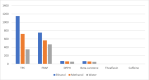
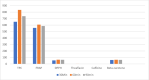
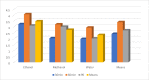
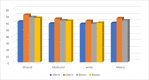
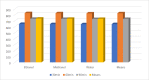
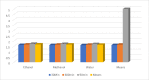
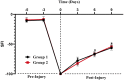
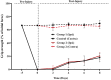
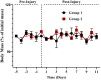
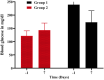
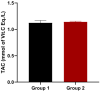
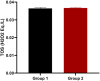
The mandate of the current investigation was to elucidate the therapeutic and antioxidant perspective of black tea. Purposely, black tea compositional analysis followed by polyphenol extraction and antioxidant characterization was done. Moreover, the theaflavin from black tea extract was also isolated through the solvent partition method. Lastly, the neuroprotective effect of isolated theaflavin was assessed through a bio-efficacy trial. The outcomes delineated that black tea showed promising nutritional composition with special reference to protein and fiber. Among the extraction solvent, ethanol performed better as compared to methanol and water likewise, higher extraction was noticed at 60 min followed by 90 and 30 min. All the extracts indicated antioxidant activity reflected through significant DPPH, TPC, FRAP, and beta carotene as-69.13 ± 3.00, 1148.92 ± 14.01, 752.44 ± 10.30, and 65.74 ± 3.28, respectively. However, isolated theaflavin exhibited higher antioxidant capacity as-737.74 ± 12.55, 82.60 ± 2.33, and 853.77 ± 9.55, for TPC, DPPH, and FRAP, respectively, as compared to extracts. In 15 days' efficacy was physically induced with sciatic nerve injury h sciatic nerve injury physically and treated with isolated theaflavin. A total of 12 healthy albino mice were randomly assigned to either the control (n = 6) or theaflavin (5.0 mg/kg (n = 6)) groups. In these groups, behavioral tests were used to assess and compare enhanced functional recovery as well as skeletal muscle mass measurement. Serum samples included oxidative stress markers. In theaflavin leaves, behavioral tests revealed a statistically significant (p < .001) improvement in sensorimotor function restoration, muscle mass restoration, a substantial decrease in TOS, a significant increase in TAC, and enhanced antioxidative enzyme activity. Considering the above-mentioned therapeutic perspectives of theaflavin, the current research was planned to optimize the isolation of theaflavin from black tea and probed for their neuroprotective effect in mice models.
Keywords: inflammatory response; neuroprotective effect; oxidative stress; theaflavin.
© 2023 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lipid peroxidation diminishing perspective of isolated theaflavins and thearubigins from black tea in arginine induced renal malfunctional rats.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jul 18;17(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0808-3. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30021615 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the potential of black tea based flavonoids against hyperlipidemia related disorders.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Mar 27;17(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0688-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29592809 Free PMC article.
-
Black Tea Extract and Its Theaflavin Derivatives Inhibit the Growth of Periodontopathogens and Modulate Interleukin-8 and β-Defensin Secretion in Oral Epithelial Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 18;10(11):e0143158. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143158. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26581041 Free PMC article.
-
Black tea polyphenol theaflavin as promising antioxidant and potential copper chelator.J Sci Food Agric. 2020 May;100(7):3126-3135. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10347. Epub 2020 Mar 6. J Sci Food Agric. 2020. PMID: 32086808
-
Multivariate effects of Chinese keemun black tea grades (Camellia sinensis var. sinensis) on the phenolic composition, antioxidant, antihemolytic and cytotoxic/cytoprotection activities.Food Res Int. 2019 Nov;125:108516. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108516. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Food Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31554085
Cited by
-
Dihydroisotanshinone I and BMAL-SIRT1 Pathway in an In Vitro 6-OHDA-Induced Model of Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 4;24(13):11088. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311088. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446264 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring lipin1 as a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.J Transl Med. 2024 Jul 16;22(1):664. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05494-z. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39014470 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophages and food safety: An updated overview.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 May 4;11(7):3621-3630. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3360. eCollection 2023 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37457180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tea and Its Active Ingredients in Preventing and Alleviating Depression: A Comprehensive Review.Foods. 2025 Jun 11;14(12):2054. doi: 10.3390/foods14122054. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40565663 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Afzaal, M. , Saeed, F. , Ateeq, H. , Akhtar, M. N. , Imran, A. , Ahmed, A. , Aamir, M. , Islam, F. , Yasmin, I. , Shah, Y. A. , Hussain, M. , Hameed, A. , Kumar, R. , & Awuchi, C. G. (2023). Probiotics encapsulated gastroprotective cross‐linked microgels: Enhanced viability under stressed conditions with dried apple carrier. Food Science & Nutrition, 11(2), 817–827. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anandhan, A. , Tamilselvam, K. , Radhiga, T. , Rao, S. , Essa, M. M. , & Manivasagam, T. (2012). Theaflavin, a black tea polyphenol, protects nigral dopaminergic neurons against chronic MPTP/probenecid induced Parkinson's disease. Brain Research, 1433, 104–113. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

