Phytobioactive compounds as therapeutic agents for human diseases: A review
- PMID: 37324906
- PMCID: PMC10261751
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3308
Phytobioactive compounds as therapeutic agents for human diseases: A review
Abstract
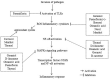
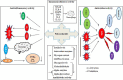
Phytobioactive compounds are plant secondary metabolites and bioactive compounds abundantly present in medicinal plants and have remarkable therapeutic potential. Oxidative stress and antibiotic resistance are major causes of present-day ailments such as diabetes, atherosclerosis, cardiovascular disorders, cancer, and inflammation. The data for this review were collected from Google Scholar, PubMed, Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ), and Science Direct by using keywords: "Medicinal plants, Phytobioactive compounds, Polyphenols, Alkaloids, Carotenoids etc." Several studies have reported the pharmacological and therapeutic potential of the phytobioactives. Polyphenols, alkaloids, terpenes, and polysaccharides isolated from medicinal plants showed remarkable antioxidant, anticancer, cytotoxic, anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, and antidiabetic activities. This literature review was planned to provide comprehensive insight into the biopharmacological and therapeutic potential of phytobioactive compounds. The techniques used for the extraction and isolation of phytobioactive compounds, and bioassays required for their biological activities such as antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxic activities, have been discussed. Characterization techniques for the structural elucidation of phytobioactive compounds such as HPLC, TLC, FTIR, GC-MS/MS, and NMR have also been discussed. This review concludes that phytobioactive compounds may be used as potential alternative to synthetic compounds as therapeutic agents for the treatment of various diseases.
Keywords: alkaloids; medicinal plants; phytobioactive compounds; polyphenols; terpenoids.
© 2023 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abbas, M. , Rana, S. , Shahid, M. , Rana, N. , Mahmood‐ul‐Hassan, M. , & Hussain, M. (2012). Chemical evaluation of weed seeds mixed with wheat grains at harvest. The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 22(2), 283–288.
-
- Abbas, M. , Shahid, M. , Sheikh, M. A. , & Muhammad, G. (2014). Phytochemical screening of plants used in folkloric medicine: Effect of extraction method and solvent. Asian Journal of Chemistry, 26(18), 6194–6198.
-
- Abbas, S. , Sharif, M. K. , Butt, M. S. , & Shahid, M. (2020). Screening of Pakistani sesame cultivars for nutritive value and bioactive components. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 57(3), 743–751.
-
- Abbasi, M. A. , Irshad, M. , Riaz, T. , Siddiqui, S. Z. , & Shahid, M. (2019). In vitro assessment of antibacterial, antifungal, enzyme inhibition and hemolytic activities of various fractions of Rhynchosia pseudo‐cajan. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 32(5), 2003–2010. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

