Limonin, a natural ERK2 agonist, protects against ischemic acute kidney injury
- PMID: 37324945
- PMCID: PMC10266085
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.82417
Limonin, a natural ERK2 agonist, protects against ischemic acute kidney injury
Abstract
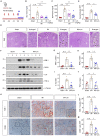
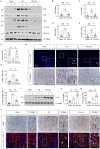
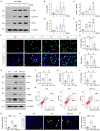
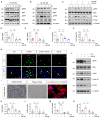
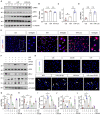
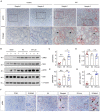
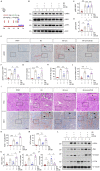
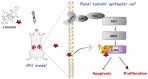
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a refractory clinical syndrome with limited effective treatments. Amid AKI, activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) cascade plays a critical role in promoting kidney repair and regeneration. However, a mature ERK agonist in treating kidney disease remains lacking. This study identified limonin, a member of the class of compounds known as furanolactones, as a natural ERK2 activator. Employing a multidisciplinary approach, we systemically dissected how limonin mitigates AKI. Compared to vehicles, pretreatment of limonin significantly preserved kidney functions after ischemic AKI. We revealed that ERK2 is a significant protein linked to the limonin's active binding sites through structural analysis. The molecular docking study showed a high binding affinity between limonin and ERK2, which was confirmed by the cellular thermal shift assay and microscale thermophoresis. Mechanistically, we further validated that limonin promoted tubular cell proliferation and reduced cell apoptosis after AKI by activating ERK signaling pathway in vivo. In vitro and ex vivo, blockade of ERK abolished limonin's capacity of preventing tubular cell death under hypoxia stress. Our results indicated that limonin is a novel ERK2 activator with strong translational potential in preventing or mitigating AKI.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; cell death; cell proliferation; extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2; limonin.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Network Pharmacology to Reveal the Molecular Mechanisms of Rutaceous Plant-derived Limonin Ameliorating Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis.Crit Rev Immunol. 2023;43(5):11-23. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2023050080. Crit Rev Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37831520
-
Limonin mitigates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through metabolic reprogramming.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Nov;167:115531. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115531. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37741252
-
Effect of the presence of berberine/curcumin on the binding of limonin to human serum albumin and antitumor activity in vitro.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2024 Dec 15;323:124929. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2024.124929. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2024. PMID: 39116592
-
Tubular transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif protects against ischemic acute kidney injury.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Jul 17;134(13):1593-1612. doi: 10.1042/CS20200223. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32558891
-
Renal tubular cell death and inflammation response are regulated by the MAPK-ERK-CREB signaling pathway under hypoxia-reoxygenation injury.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2019 Oct-Dec;39(5-6):383-391. doi: 10.1080/10799893.2019.1698050. Epub 2019 Nov 29. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2019. PMID: 31782334 Review.
Cited by
-
Euodiae Fructus: a review of botany, application, processing, phytochemistry, quality control, pharmacology, and toxicology.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 29;16:1509032. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1509032. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39944619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy Dysfunction: The Kernel of Hair Loss?Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024 May 20;17:1165-1181. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S462294. eCollection 2024. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38800357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nephroprotective effects of substances of medicine food homology and traditional Chinese medicine phytochemicals against acute kidney injury.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 19;16:1539886. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1539886. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40046749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the Mechanism of Action of the Degraded Limonoid Prieurianin.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 22;25(7):3597. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073597. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the effects of apelin-13 on renal function and NHE3 activity following ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury.Front Physiol. 2025 Mar 19;16:1544274. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1544274. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40177358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rewa O, Bagshaw SM. Acute kidney injury-epidemiology, outcomes and economics. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014;10:193–207. - PubMed
-
- Ronco C, Bellomo R, Kellum JA. Acute kidney injury. Lancet (London, England) 2019;394:1949–64. - PubMed
-
- Kellum JA, Romagnani P, Ashuntantang G, Ronco C, Zarbock A, Anders HJ. Acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:52. - PubMed
-
- Bagshaw SM, Wald R, Adhikari NKJ, Bellomo R, da Costa BR, Dreyfuss D. et al. Timing of Initiation of Renal-Replacement Therapy in Acute Kidney Injury. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:240–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

