Indian research on transcranial magnetic stimulation: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 37325097
- PMCID: PMC10263091
- DOI: 10.4103/indianjpsychiatry.indianjpsychiatry_678_22
Indian research on transcranial magnetic stimulation: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: A significant body of evidence on the role of TMS in neurology and psychiatry has emerged from Indian studies.
Aims: We aimed to assess the existing and emerging trends of research on TMS as a diagnostic or therapeutic tool in India using bibliometric analysis.
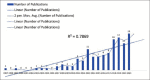
Results: A total of 146 publications, retrieved from various databases, were analyzed using Microsoft Excel and VOSviewer. We found a linear positive growth of publications in India in the field of TMS and neuropsychiatry, with about 3000 citations so far. The most researched diagnosis was schizophrenia. NIMHANS, Bengaluru, had the highest number of publications. The journal with the highest number of publications was the Asian Journal of Psychiatry, and that with the highest citations was the Journal of Affective disorders.
Conclusion: The growth of Indian research in the field of TMS corresponds to that of the global one but also suggests the need for more studies to match the research output from other countries.
Keywords: Noninvasive brain stimulation; publications; scientometry; trend.
Copyright: © 2023 Indian Journal of Psychiatry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gururaj G, Varghese M, Benegal V, Rao GN, Pathak K, Singh LK, et al. National Mental Health Survey of India, 2015–16: Prevalence, Patterns and Outcomes (Publication No. 129) Bengaluru: National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences; 2016.
-
- Mishra BR, Nizamie SH, Das B, Praharaj SK. Efficacy of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in alcohol dependence: A sham-controlled study. Addiction. 2010;105:49–55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources