Serum Amyloid A: A Potential New Marker of Severity in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- PMID: 37325280
- PMCID: PMC10264916
- DOI: 10.1159/000528658
Serum Amyloid A: A Potential New Marker of Severity in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Skin Appendage Disord. 2024 Aug;10(4):333. doi: 10.1159/000539351. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Skin Appendage Disord. 2024. PMID: 39210940 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease with systemic inflammation and high impact on quality of life. Treatment strategies are still inadequate with a lack of inflammation biomarkers. We conducted a prospective study to assess the correlation between serum amyloid A (SAA) levels and active lesion count; disease severity; Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI); smoking; BMI; and lesion sites.
Methods: Forty-one patients (M/F: 22/19) were enrolled. Demographic, clinical, laboratory, and therapeutic data were assessed at baseline on patients not under treatment or in wash-out from systemic treatment for at least 2 weeks. Associations were investigated by univariate and multivariate analyses.
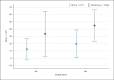
Results: SAA levels were significantly associated with number of nodules (p = 0.005), abscesses (p < 0.001), fistulas (p = 0.016), and severe IHS4 (p = 0.088 and r = 0.514). Gluteal localization was correlated with high values of mSartorius and severe IHS4.
Conclusions: We recommend assessment of SAA levels to monitor therapeutic response in patient with HS in order to prevent disease's flare and potential complications.
Keywords: Acne inversa; Biomarker; Hidradenitis suppurativa; Inflammation; Inflammatory skin disease; Serum amyloid A.
Copyright © 2023 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Witte-Händel E, Wolk K, Tsaousi A, Irmer ML, Mosner R, Shomroni O, et al. The IL-1 pathway is hyperactive in hidradenitis suppurativa and contributes to skin infiltration and destruction. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139((6)):1294–1305. - PubMed
-
- Amur A. Biomarker terminology speaking the same language. US Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/files/BIOMARKER-TERMINOLOGY–SPEAKING-THE-SAME-LANGUA... (accessed November 18, 2022). [Google Scholar]
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources